The Role of Secretory Pathways in Candida albicans Pathogenesis
- PMID: 32102426
- PMCID: PMC7151058
- DOI: 10.3390/jof6010026
The Role of Secretory Pathways in Candida albicans Pathogenesis
Abstract
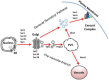
Candida albicans is a fungus that is a commensal organism and a member of the normal human microbiota. It has the ability to transition into an opportunistic invasive pathogen. Attributes that support pathogenesis include secretion of virulence-associated proteins, hyphal formation, and biofilm formation. These processes are supported by secretion, as defined in the broad context of membrane trafficking. In this review, we examine the role of secretory pathways in Candida virulence, with a focus on the model opportunistic fungal pathogen, Candida albicans.
Keywords: Candida albicans; biofilm; filamentation; pathogenesis; secretion; trafficking; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
None to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Neville B.W. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Saunders/Elsevier; St. Louis, MO, USA: 2009.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

