Influence of a Selenium Biofortification on Antioxidant Properties and Phenolic Compounds of Apples (Malus domestica)
- PMID: 32102431
- PMCID: PMC7070929
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9020187
Influence of a Selenium Biofortification on Antioxidant Properties and Phenolic Compounds of Apples (Malus domestica)
Abstract
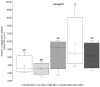
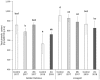
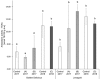
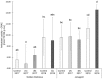
Biofortified apples seem to be a suitable produce. In this study, different selenium forms and application levels were applied to the two apple varieties 'Golden Delicious' and 'Jonagold', grown in the years 2017 and 2018 in order to increase the selenium uptake within a typical Western diet. It was shown that the biofortification, which was performed as a foliar application implemented in usual calcium fertilization, led to significantly increased selenium contents in the fruits. Furthermore, biofortification affected the total phenolic content (TPC), the polyphenol oxidase activity (PPO), as well as the antioxidant activity (AOA), the latter measured with the two well-known assays Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity Assay (TEAC) and Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity Assays (ORAC). The varying selenium forms and application levels showed a differing influence on the parameters mentioned before. Higher fertilizer levels resulted in higher selenium accumulation. It was found that PPO activity fluctuates less in biofortified apples. With regard to TPC, selenate led to higher amounts when compared to the untreated controls and selenite resulted in lower TPC. AOA analysis showed no clear tendencies as a result of the selenium biofortification. In the case of 'Jonagold', a higher AOA was generally measured when being biofortified, whereas, in the case of 'Golden Delicious', only one form of application led to higher AOA. Additionally, differences in the amount of major phenolic compounds, measured with High Performance Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn), were observed, depending on the conditions of the biofortification and the variety.
Keywords: TEAC; Total Phenolic Content; agronomic biofortification; antioxidant activity; apple; phenolic compounds; phenoloxidase; selenium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship between Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Properties, and the Allergenic Protein Mal d 1 in Different Selenium-Biofortified Apple Cultivars (Malus domestica).Molecules. 2021 Apr 30;26(9):2647. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092647. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33946582 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium biofortification of different varieties of apples (Malus domestica) - Influence on protein content and the allergenic proteins Mal d 1 and Mal d 3.Food Chem. 2021 Nov 15;362:130134. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130134. Epub 2021 May 16. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 34087709
-
Effect of foliar application with sodium selenate on selenium biofortification and fruit quality maintenance of 'Starking Delicious' apple during storage.J Sci Food Agric. 2019 Aug 30;99(11):5149-5156. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9761. Epub 2019 Jun 13. J Sci Food Agric. 2019. PMID: 31032929
-
[Evaluation of antioxidant activity of fresh apples different pomological varieties after treatment with ionizing radiation].Vopr Pitan. 2018;87(3):66-71. doi: 10.24411/0042-8833-2018-10044. Epub 2018 May 11. Vopr Pitan. 2018. PMID: 30592882 Review. Russian.
-
Selenium Biofortification of Agricultural Crops and Effects on Plant Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds Important for Human Health and Disease Prevention - a Review.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2019 Dec;74(4):449-460. doi: 10.1007/s11130-019-00769-z. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31522406 Review.
Cited by
-
Agronomic and Genetic Strategies to Enhance Selenium Accumulation in Crops and Their Influence on Quality.Foods. 2023 Dec 11;12(24):4442. doi: 10.3390/foods12244442. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38137246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"An apple a day keeps the doctor away": The potentials of apple bioactive constituents for chronic disease prevention.J Food Sci. 2022 Jun;87(6):2291-2309. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16155. Epub 2022 May 3. J Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 35502671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of preharvest sprays of iodine, selenium and calcium on apple biofortification and their quality and storability.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 9;18(3):e0282873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282873. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36893128 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced accumulation of phenolics in pea (Pisum sativum L.) seeds upon foliar application of selenate or zinc oxide.Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 30;10:1083253. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1083253. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37063310 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Milk Kefirs Obtained from Cow's, Ewe's and Goat's Milk: Antioxidant Role of Microbial-Derived Exopolysaccharides.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 11;13(3):335. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030335. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lawson P.G., Daum D., Czauderna R., Vorsatz C. Factors influencing the efficacy of iodine foliar sprays used for biofortifying butterhead lettuce (Lactuca sativa) J. Plant Nutr. Sci. 2016;179:661–669. doi: 10.1002/jpln.201600213. - DOI
-
- Cakmak I. Agronomic Approaches in Biofortification of Food Crops with Micronutrients. UC Davis: Department of Plant Sciences; Davis, CA, USA: 2009.
-
- Poňavič M., Scheib A. Distribution of selenium in European agricultural and grazing land soil. In: Reimann C., Birke M., Demetriades A., Filzmoser P., O’Connor P., editors. Chemistry of Europe’s Agricultural Soils. Vol. 103. Geologisches Jahrbuch (Reihe B), Schweizerbart; Stuttgart, Germany: 2014. pp. 131–144.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

