Clinico-Biological Implications of Modified Levels of Cytokines in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Possible Therapeutic Role
- PMID: 32102441
- PMCID: PMC7072434
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12020524
Clinico-Biological Implications of Modified Levels of Cytokines in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Possible Therapeutic Role
Abstract
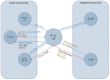
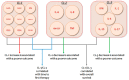
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) is the main cause of mortality among hematologic diseases in Western nations. B-CLL is correlated with an intense alteration of the immune system. The altered functions of innate immune elements and adaptive immune factors are interconnected in B-CLL and are decisive for its onset, evolution, and therapeutic response. Modifications in the cytokine balance could support the growth of the leukemic clone via a modulation of cellular proliferation and apoptosis, as some cytokines have been reported to be able to affect the life of B-CLL cells in vivo. In this review, we will examine the role played by cytokines in the cellular dynamics of B-CLL patients, interpret the contradictions sometimes present in the literature regarding their action, and evaluate the possibility of manipulating their production in order to intervene in the natural history of the disease.
Keywords: B lymphocyte; T lymphocyte; chronic lymphocytic leukemia; cytokine; immune system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gonzalez-Rodriguez A.P., Contesti J., Huergo-Zapico L., Lopez-Soto A., Fernandez-Guizan A., Acebes-Huerta A., Gonzalez-Huerta A.J., Gonzalez E., Fernandez-Alvarez C., Gonzalez S. Prognostic significance of CD8 and CD4 T cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2010;51:1829–1836. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2010.503820. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Palmer S., Hanson C.A., Zent C.S., Porrata L.F., LaPlant B., Geyer S.M., Markovic S.N., Call T.G., Bowen D.A., Diane F., et al. Prognostic importance of T and NK-cells in a consecutive series of newly diagnosed patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2008;141:607–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07070.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huergo-Zapico L., Acebes-Huerta A., Gonzalez-Rodriguez A.P., Contesti J., Gonzalez-Garcıa E., Payer A.R., Villa-Alvarez M., Fernandez-Guizan A., Lopez-Soto A., Gonzalez S. Expansion of NK cells and reduction of NKG2D expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Correlation with progressive disease. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e108326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108326. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

