Osteopontin and iCD8α Cells Promote Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte Homeostasis
- PMID: 32102904
- PMCID: PMC7175606
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901168
Osteopontin and iCD8α Cells Promote Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte Homeostasis
Abstract
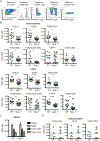
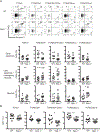
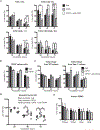
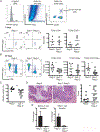
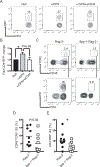
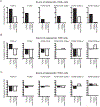
Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL) comprise a diverse population of cells residing in the epithelium at the interface between the intestinal lumen and the sterile environment of the lamina propria. Because of this anatomical location, IEL are considered critical components of intestinal immune responses. Indeed, IEL are involved in many different immunological processes, ranging from pathogen control to tissue stability. However, despite their critical importance in mucosal immune responses, very little is known about the homeostasis of different IEL subpopulations. The phosphoprotein osteopontin is important for critical physiological processes, including cellular immune responses, such as survival of Th17 cells and homeostasis of NK cells among others. Because of its impact in the immune system, we investigated the role of osteopontin in the homeostasis of IEL. In this study, we report that mice deficient in the expression of osteopontin exhibit reduced numbers of the IEL subpopulations TCRγδ+, TCRβ+CD4+, TCRβ+CD4+CD8α+, and TCRβ+CD8αα+ cells in comparison with wild-type mice. For some IEL subpopulations, the decrease in cell numbers could be attributed to apoptosis and reduced cell division. Moreover, we show in vitro that exogenous osteopontin stimulates the survival of murine IEL subpopulations and unfractionated IEL derived from human intestines, an effect mediated by CD44, a known osteopontin receptor. We also show that iCD8α IEL but not TCRγδ+ IEL, TCRβ+ IEL, or intestinal epithelial cells, can promote survival of different IEL populations via osteopontin, indicating an important role for iCD8α cells in the homeostasis of IEL.
Copyright © 2020 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unconventional Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocytes in Health and Disease.Crit Rev Immunol. 2021;41(4):23-38. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2021039957. Crit Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35381141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate CD8αα+ cells promote ILC1-like intraepithelial lymphocyte homeostasis and intestinal inflammation.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 10;14(7):e0215883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215883. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31291255 Free PMC article.
-
Natural intraepithelial lymphocyte populations rise during necrotic enteritis in chickens.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 22;15:1354701. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354701. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38455042 Free PMC article.
-
Functionally active CD8alphabeta+ TCRgammadelta intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in athymic nu/nu mice.Int Immunol. 2004 Jan;16(1):111-7. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh008. Int Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14688066
-
The interaction of intestinal epithelial cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes in host defense.Immunol Res. 1999;20(3):219-35. doi: 10.1007/BF02790405. Immunol Res. 1999. PMID: 10741862 Review.
Cited by
-
Unconventional Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocytes in Health and Disease.Crit Rev Immunol. 2021;41(4):23-38. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2021039957. Crit Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35381141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carnosol Maintains Intestinal Barrier Function and Mucosal Immune Homeostasis in DSS-Induced Colitis.Front Nutr. 2022 May 24;9:894307. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.894307. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35685885 Free PMC article.
-
The immune duality of osteopontin and its therapeutic implications for kidney transplantation.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 28;16:1520777. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1520777. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40093009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alkaline sphingomyelinase (NPP7) impacts the homeostasis of intestinal T lymphocyte populations.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 19;13:1050625. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1050625. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36741374 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized phospholipids cause changes in jejunum mucus that induce dysbiosis and systemic inflammation.J Lipid Res. 2022 Jan;63(1):100153. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100153. Epub 2021 Nov 20. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 34808192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Talayero P, Mancebo E, Calvo-Pulido J, Rodriguez-Munoz S, Bernardo I, Laguna-Goya R, Cano-Romero FL, Garcia-Sesma A, Loinaz C, Jimenez C, Justo I, and Paz-Artal E. 2016. Innate Lymphoid Cells Groups 1 and 3 in the Epithelial Compartment of Functional Human Intestinal Allografts. Am J Transplant 16: 72–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

