Activating low-temperature diesel oxidation by single-atom Pt on TiO2 nanowire array
- PMID: 32102998
- PMCID: PMC7044320
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-14816-w
Activating low-temperature diesel oxidation by single-atom Pt on TiO2 nanowire array
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Activating low-temperature diesel oxidation by single-atom Pt on TiO2 nanowire array.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 9;11(1):1317. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15227-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32152286 Free PMC article.
Abstract
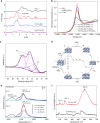
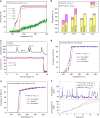
Supported metal single atom catalysts (SACs) present an emerging class of low-temperature catalysts with high reactivity and selectivity, which, however, face challenges on both durability and practicality. Herein, we report a single-atom Pt catalyst that is strongly anchored on a robust nanowire forest of mesoporous rutile titania grown on the channeled walls of full-size cordierite honeycombs. This Pt SAC exhibits remarkable activity for oxidation of CO and hydrocarbons with 90% conversion at temperatures as low as ~160 oC under simulated diesel exhaust conditions while using 5 times less Pt-group metals than a commercial oxidation catalyst. Such an excellent low-temperature performance is sustained over hydrothermal aging and sulfation as a result of highly dispersed and isolated active single Pt ions bonded at the Ti vacancy sites with 5 or 6 oxygen ions on titania nanowire surfaces.
Conflict of interest statement
A U.S. non-provisional patent (Application No.: 16/465,981) on catalyst methods of making, with P.-X.G. and S.H. as co-inventors, has been filed by the University of Connecticut.
Figures

References
-
- Mellor JR, et al. The application of supported gold catalysts to automotive pollution abatement. Catal. Today. 2002;72:145–156. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(01)00488-6. - DOI
-
- Li J, Chang H, Ma L, Hao J, Yang RT. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts—a review. Catal. Today. 2011;175:147–156. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.034. - DOI
-
- Liu G, Gao P-X. A review of NOx storage/reduction catalysts: mechanism, materials and degradation studies. Catal. Sci. Tech. 2011;1:552–568. doi: 10.1039/c1cy00007a. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

