FTY720 Protects Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Preventing the Redistribution of Tight Junction Proteins and Decreases Inflammation in the Subacute Phase in an Experimental Stroke Model
- PMID: 32103462
- PMCID: PMC7496052
- DOI: 10.1007/s12975-020-00789-x
FTY720 Protects Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Preventing the Redistribution of Tight Junction Proteins and Decreases Inflammation in the Subacute Phase in an Experimental Stroke Model
Abstract
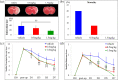
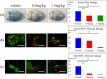
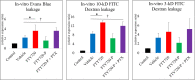
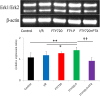
Injury due to brain ischemia followed by reperfusion (I/R) may be an important therapeutic target in the era of thrombectomy. FTY720, a widely known sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonist, exerts various neuroprotective effects. The aim of this study was to examine the protective effect of FTY720 with respect to I/R injury, especially focusing on blood-brain barrier (BBB) protection and anti-inflammatory effects. Male rats were subjected to transient ischemia and administered vehicle or 0.5 or 1.5 mg/kg of FTY720 immediately before reperfusion. Positron emission tomography (PET) with [18F]DPA-714 was performed 2 and 9 days after the insult to serially monitor neuroinflammation. Bovine and rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (MVECs) were also subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) and reperfusion, and administered FTY720, phosphorylated-FTY720 (FTY720-P), or their inhibitor. FTY720 dose-dependently reduced cell death, the infarct size, cell death including apoptosis, and inflammation. It also ameliorated BBB disruption and neurological deficits compared to in the vehicle group. PET indicated that FTY720 significantly inhibited the worsening of inflammation in later stages. FTY720-P significantly prevented the intracellular redistribution of tight junction proteins but did not increase their mRNA expression. These results suggest that FTY720 can ameliorate I/R injury by protecting the BBB and regulating neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Blood–brain barrier; Brain ischemia–reperfusion; FTY720; Inflammation; Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Anderson L, Truelsen T, O'Donnell M, Venketasubramanian N, Barker-Collo S, Lawes CM, Wang W, Shinohara Y, Witt E, Ezzati M, Naghavi M, Murray C, Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2010 (GBD 2010) and the GBD Stroke Experts Group Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2014;383(9913):245–254. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61953-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Albers GW, Cognard C, Cohen DJ, Hacke W, Jansen O, Jovin TG, Mattle HP, Nogueira RG, Siddiqui AH, Yavagal DR, Baxter BW, Devlin TG, Lopes DK, Reddy VK, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Singer OC, Jahan R, SWIFT PRIME Investigators Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(24):2285–2295. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1415061. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, Yan B, Dowling RJ, Parsons MW, Oxley TJ, Wu TY, Brooks M, Simpson MA, Miteff F, Levi CR, Krause M, Harrington TJ, Faulder KC, Steinfort BS, Priglinger M, Ang T, Scroop R, Barber PA, McGuinness B, Wijeratne T, Phan TG, Chong W, Chandra RV, Bladin CF, Badve M, Rice H, de Villiers L, Ma H, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM, EXTEND-IA Investigators Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(11):1009–1018. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414792. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, Roy D, Jovin TG, Willinsky RA, Sapkota BL, Dowlatshahi D, Frei DF, Kamal NR, Montanera WJ, Poppe AY, Ryckborst KJ, Silver FL, Shuaib A, Tampieri D, Williams D, Bang OY, Baxter BW, Burns PA, Choe H, Heo JH, Holmstedt CA, Jankowitz B, Kelly M, Linares G, Mandzia JL, Shankar J, Sohn SI, Swartz RH, Barber PA, Coutts SB, Smith EE, Morrish WF, Weill A, Subramaniam S, Mitha AP, Wong JH, Lowerison MW, Sajobi TT, Hill MD, ESCAPE Trial Investigators Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(11):1019–1030. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414905. - DOI - PubMed

