Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects of Metal Nanoparticles in Combination with Antibiotics Against Some Reference Strains of Pathogenic Microorganisms
- PMID: 32104007
- PMCID: PMC7012269
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S234425
Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects of Metal Nanoparticles in Combination with Antibiotics Against Some Reference Strains of Pathogenic Microorganisms
Abstract
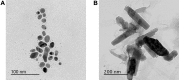
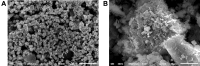
Background and aim: Nanosized inorganic antibacterial materials have received increasing attention in recent years. The present study aimed to determine the antimicrobial activity of silver (Ag) and zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles alone and in combination with antibiotics against reference strains of pathogenic microorganisms as Staphylococcus aureus (Staph. aureus), Salmonella enterica subsp. Bukuru, Escherichia coli (E.coli) and Candida albicans ( C. albicans).
Methods: The antimicrobial effect of metal-nanoparticles (AgNPs and ZnONPS) and in combination with antibiotics was studied using the normal disc-diffusion method.
Results: Both AgNPs and ZnONPs had increased antibacterial activity with an increase in their concentration against Gram-positive bacterium (Staph. aureus), Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli and Salmonella spp) and no effect on C. albicans. The synergistic effect of antibiotics (azithromycin, cefotaxime, cefuroxime, fosfomycin and chloramphenicol) against E. coli was significantly increased in the presence of AgNPs compared to antibiotic only. However, all antibiotics had a synergistic effect in the presence of AgNps against Salmonella spp. On the other hand, the antibacterial action of AgNPs with oxacillin and neomycin antibiotics against Staph. aureus was significantly decreased in comparison with antibiotics only. The synergistic effect of antibiotics (azithromycin, oxacillin, cefotaxime, cefuroxime, fosfomycin and oxytetracycline) against E. coli was significantly increased in presence of ZnONPs compared to antibiotic only and also the synergistic effect of antibiotics (azithromycin, cefotaxime, cefuroxime, fosfomycin, chloramphenicol and oxytetracycline) against Staph. aureus was significantly increased in the presence of ZnONPs compared to antibiotics only. On the other hand, most antibiotics had an antagonistic effect in presence of ZnONps against Salmonella spp.
Conclusion: AgNPs and ZnONPs demonstrate a good synergistic effect with antibiotics and this may open the door for a future combination therapy against pathogenic bacteria.
Keywords: AgNPs; Candida albicans; Salmonella spp; ZnONPs; antimicrobial activity E. coli Staph. aureus.
© 2020 Abo-Shama et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brosset E. The law of the European U nion on nanotechnologies: comments on a paradox. Rev Eur Comp Int Environ Law. 2013;22(2):155–162. doi: 10.1111/reel.12030 - DOI
-
- Madhuri S, Maheshwar S, Sunil P, Oza G. Nanotechnology: Concepts and Applications. USA: CRC Press; 2012.
-
- Abd Ellah NH, Ahmed EA, Abd-Ellatief RB, Ali MF, Zahran AM, Hetta HF. Metoclopramide nanoparticles modulate immune response in a diabetic rat model: association with regulatory T cells and proinflammatory cytokines. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:2383–2395. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S196842 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous