Determination of the ED50 and ED95 of intravenous bolus of norepinephrine for the treatment of hypotension during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery
- PMID: 32104231
- PMCID: PMC7027136
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8360
Determination of the ED50 and ED95 of intravenous bolus of norepinephrine for the treatment of hypotension during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery
Abstract
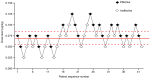
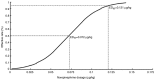
Norepinephrine is considered as a potential alternative for blood pressure stabilization during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery, as it maintains a better maternal heart rate and cardiac output compared with phenylephrine. However, its use as a bolus dose for hypotension treatment remains largely unexplored. Therefore, the present study investigated the ED50 and ED95 of norepinephrine as a bolus for maternal hypotension during cesarean delivery. In the present prospective trial, 42 patients were enrolled for elective delivery under spinal anesthesia. The dose of norepinephrine was decided by the up-and-down sequential allocation method (UDM) with an initial dose of 0.075 µg/kg and a 0.025 µg/kg increment. The 42 patients received a bolus of norepinephrine when systolic blood pressure fell to <80% of baseline. The ED50 was calculated by the sequential method and the probit regression model. The ED95 was then calculated using the probit regression model. The ED50 of norepinephrine, which was determined by the UDM, was 0.067 µg/kg (95% CI, 0.056-0.081). The probit regression model calculated an ED50 of 0.072 µg/kg (95% CI, 0.056-0.088) and an ED95 of 0.121 µg/kg (95% CI, 0.1-0.207). In summary, the present results suggested the ED50 of a bolus norepinephrine for preventing hypotension in elective CD is 0.067 µg/kg (95% CI, 0.056-0.081), with an ED95 of 0.121 µg/kg (95% CI, 0.1-0.207).
Keywords: cesarean section; norepinephrine; spinal anesthesia.
Copyright: © Wang et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ED50 and ED95 of Prophylactic Norepinephrine for Preventing Post-Spinal Hypotension During Cesarean Delivery Under Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia: A Prospective Dose-Finding Study.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 12;12:691809. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.691809. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34322021 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine Intermittent Intravenous Boluses to Prevent Hypotension During Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery: A Sequential Allocation Dose-Finding Study.Anesth Analg. 2017 Jul;125(1):212-218. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001846. Anesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 28248702
-
A Random-allocation Graded Dose-Response Study of Norepinephrine and Phenylephrine for Treating Hypotension during Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery.Anesthesiology. 2017 Dec;127(6):934-941. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001880. Anesthesiology. 2017. PMID: 28872480 Clinical Trial.
-
Minimum Effective Dose (ED50 and ED95) of Intrathecal Hyperbaric Bupivacaine for Cesarean Delivery: A Systematic Review.AANA J. 2018 Oct;86(5):348-360. AANA J. 2018. PMID: 31584404
-
Prophylactic intravenous norepinephrine for the prevention of hypotension during spinal anesthesia for elective cesarean section: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 19;14:1247214. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1247214. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37795034 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Novel Trajectories Towards Possible Effects of Semaglutide for Amelioration of Reserpine-induced Fibromyalgia in Rats: Contribution of cAMP/PKA/p-CREB and M1/M2 Microglia Polarization.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 17;20(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10196-4. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40240584 Free PMC article.
-
Up-and-down determination of prophylactic norepinephrine boluses combined with crystalloid co-load for preventing post-spinal anesthesia hypotension during cesarean section.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Jan 25;25(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-02913-6. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39856541 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Scoping Review: Is Push-Dose Norepinephrine a Better Choice?West J Emerg Med. 2024 Sep;25(5):708-714. doi: 10.5811/westjem.18584. West J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39319801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mercier FJ, Augè M, Hoffmann C, Fischer C, Gouez AL. Maternal hypotension during spinal anesthesia for caesarean delivery. Minerva Anestesiol. 2013;79:62–73. - PubMed
-
- Ngan Kee WD, Lee A, Khaw KS, Ng FF, Karmakar MK, Gin T. A randomized double-blinded comparison of phenylephrine and ephedrine infusion combinations to maintain blood pressure during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery: The effects on fetal acid-base status and hemodynamic control. Anesth Analg. 2008;107:1295–1302. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31818065bc. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
