Clinical significance of serum levels of microRNA-27a and its correlation with interleukin-10 in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome caused by acute paraquat poisoning
- PMID: 32104255
- PMCID: PMC7027156
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.8409
Clinical significance of serum levels of microRNA-27a and its correlation with interleukin-10 in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome caused by acute paraquat poisoning
Abstract
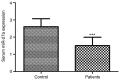
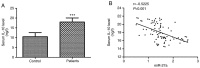
The aims of the present study were to examine the clinical significance of serum microRNA-27a (miR-27a) levels in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) caused by acute paraquat poisoning and to investigate the correlation between miR-27a and interleukin (IL)-10. A total of 82 patients with MODS induced by acute paraquat poisoning and 88 healthy controls were recruited in the present study. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR was used to measure serum miR-27a expression levels in patients with MODS and the control group. IL-10 serum levels were determined using ELISA. Decreased serum miR-27a level and increased IL-10 expression levels were detected in patients with paraquat poisoning compared with healthy controls (P<0.001). A moderately negative correlation was identified between the serum expression levels of miR-27a and IL-10 (r=-0.5225; P<0.001). miR-27a expression level was found to be associated with blood urea nitrogen, partial pressure of carbon dioxide, arterial blood lactic acid, and the acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II score (APACHE II; P<0.05). The area under the curve for miR-27a was 0.946, with a sensitivity of 86.6% and specificity of 87.5% at a cutoff value of 2.10. The non-survival patient group had lower miR-27a expression levels compared with the survival group (P<0.01). Multivariate Cox regression analyses suggested miR-27a expression level and APACHE II score were independent prognostic factors for 30-day mortality (P<0.01). The present results suggested that serum miR-27a level may be a potential novel diagnostic and prognostic factor for MODS caused by paraquat poisoning. Collectively, miR-27a may be involved in the process of MODS induced by paraquat poisoning by regulating the inflammatory response.
Keywords: diagnosis; microRNA-27a; multiple organ dysfunction syndrome; paraquat poisoning; prognosis.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures


References
-
- Flechel A, Jolivet A, Boukhari R, Misslin-Tritsch C, Manca MF, Wiel E, Megarbane B, Pousset F. Paraquat poisoning in Western French Guyana: A public health problem persisting ten years after its withdrawal from the French market. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:7034–7038. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
