Small GTPases: Structure, biological function and its interaction with nanoparticles
- PMID: 32104436
- PMCID: PMC7032109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2018.06.004
Small GTPases: Structure, biological function and its interaction with nanoparticles
Abstract
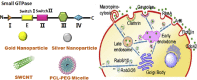
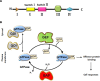
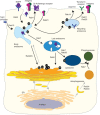
Small GTPase is a kind of GTP-binding protein commonly found in eukaryotic cells. It plays an important role in cytoskeletal reorganization, cell polarity, cell cycle progression, gene expression and many other significant events in cells, such as the interaction with foreign particles. Therefore, it is of great scientific significance to understand the biological properties of small GTPases as well as the GTPase-nano interplay, since more and more nanomedicine are supposed to be used in biomedical field. However, there is no review in this aspect. This review summarizes the small GTPases in terms of the structure, biological function and its interaction with nanoparticles. We briefly introduced the various nanoparticles such as gold/silver nanoparticles, SWCNT, polymeric micelles and other nano delivery systems that interacted with different GTPases. These current nanoparticles exhibited different pharmacological effect modes and various target design concepts in the small GTPases study. This will help to elucidate the conclusion that the therapeutic strategy targeting small GTPases might be a new research direction. It is believed that the in-depth study on the functional mechanism of GTPases can provide insights for the design and study of nanomedicines.
Keywords: Nanoparticles; Rab; Ras; Rho; Small GTPase.
© 2018 Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC. Evolution of the Rab family of small GTP-binding proteins. J Mol Biol. 2001;313(4):889–901. - PubMed
-
- Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990;348(6297):125–132. - PubMed
-
- Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC. The mammalian Rab family of small GTPases: definition of family and subfamily sequence motifs suggests a mechanism for functional specificity in the Ras superfamily. J Mol Biol. 2000;301(4):1077–1087. - PubMed
-
- Reuther GW, Der CJ. The Ras branch of small GTPases: Ras family members don't fall far from the tree. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000;12(2):157–165. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

