ROS-responsive nano-drug delivery system combining mitochondria-targeting ceria nanoparticles with atorvastatin for acute kidney injury
- PMID: 32104507
- PMCID: PMC7019163
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.40395
ROS-responsive nano-drug delivery system combining mitochondria-targeting ceria nanoparticles with atorvastatin for acute kidney injury
Abstract
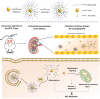
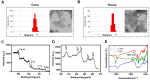
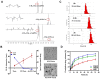
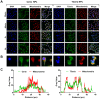
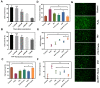
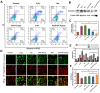
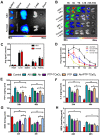
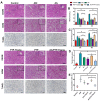
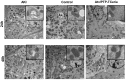
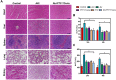
Acute kidney injury (AKI) caused by sepsis is a serious disease which mitochondrial oxidative stress and inflammatory play a key role in its pathophysiology. Ceria nanoparticles hold strong and recyclable reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging activity, have been applied to treat ROS-related diseases. However, ceria nanoparticles can't selectively target mitochondria and the ultra-small ceria nanoparticles are easily agglomerated. To overcome these shortcomings and improve therapeutic efficiency, we designed an ROS-responsive nano-drug delivery system combining mitochondria-targeting ceria nanoparticles with atorvastatin for acute kidney injury. Methods: Ceria nanoparticles were modified with triphenylphosphine (TCeria NPs), followed by coating with ROS-responsive organic polymer (mPEG-TK-PLGA) and loaded atorvastatin (Atv/PTP-TCeria NPs). The physicochemical properties, in vitro drug release profiles, mitochondria-targeting ability, in vitro antioxidant, anti-apoptotic activity and in vivo treatment efficacy of Atv/PTP-TCeria NPs were examined. Results: Atv/PTP-TCeria NPs could accumulate in kidneys and hold a great ability to ROS-responsively release drug and TCeria NPs could target mitochondria to eliminate excessive ROS. In vitro study suggested Atv/PTP-TCeria NPs exhibited superior antioxidant and anti-apoptotic activity. In vivo study showed that Atv/PTP-TCeria NPs effectively decreased oxidative stress and inflammatory, could protect the mitochondrial structure, reduced apoptosis of tubular cell and tubular necrosis in the sepsis-induced AKI mice model. Conclusions: This ROS-responsive nano-drug delivery system combining mitochondria-targeting ceria nanoparticles with atorvastatin has favorable potentials in the sepsis-induced AKI therapy.
Keywords: ROS-responsive; acute kidney injury; ceria; mitochondria-targeting.; oxidative stress.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced efficiency of mitochondria-targeted peptide SS-31 for acute kidney injury by pH-responsive and AKI-kidney targeted nanopolyplexes.Biomaterials. 2019 Aug;211:57-67. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.04.034. Epub 2019 May 6. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 31085359
-
Ceria Nanozymes with Preferential Renal Uptake for Acute Kidney Injury Alleviation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Dec 23;12(51):56830-56838. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c17579. Epub 2020 Dec 15. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 33319561
-
Mitochondria-Targeting Ceria Nanoparticles as Antioxidants for Alzheimer's Disease.ACS Nano. 2016 Feb 23;10(2):2860-70. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b08045. Epub 2016 Feb 10. ACS Nano. 2016. PMID: 26844592
-
Triphenylphosphonium (TPP)-Based Antioxidants: A New Perspective on Antioxidant Design.ChemMedChem. 2020 Mar 5;15(5):404-410. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201900695. Epub 2020 Feb 11. ChemMedChem. 2020. PMID: 32020724 Review.
-
The Advances of Ceria Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications in Orthopaedics.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Sep 29;15:7199-7214. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S270229. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33061376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Passively-targeted mitochondrial tungsten-based nanodots for efficient acute kidney injury treatment.Bioact Mater. 2022 Sep 14;21:381-393. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.08.022. eCollection 2023 Mar. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 36185743 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimmune modulating and energy supporting nanozyme-mimic scaffold synergistically promotes axon regeneration after spinal cord injury.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 5;22(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02594-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38970101 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Green Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles for Potential Therapeutic Applications: Circumstantial Insight on Mechanistic Aspects.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jun 20;12(12):2117. doi: 10.3390/nano12122117. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tubular Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 12;11(7):1356. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071356. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium nanoparticles alleviate ischemia reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury by modulating GPx-1/NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway.Theranostics. 2022 May 9;12(8):3882-3895. doi: 10.7150/thno.70830. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35664065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kellum JA, Prowle JR. Paradigms of acute kidney injury in the intensive care setting. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14:217–30. - PubMed
-
- Heemskerk S, Masereeuw R, Russel FG, Pickkers P. Selective iNOS inhibition for the treatment of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2009;5:629–40. - PubMed
-
- Thomas ME, Blaine C, Dawnay A, Devonald MA, Ftouh S, Laing C. et al. The definition of acute kidney injury and its use in practice. Kidney Int. 2015;87:62–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

