Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study
- PMID: 32105637
- PMCID: PMC7159053
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30086-4
Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study
Abstract
Background: A cluster of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia caused by infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) were successively reported in Wuhan, China. We aimed to describe the CT findings across different timepoints throughout the disease course.
Methods: Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (confirmed by next-generation sequencing or RT-PCR) who were admitted to one of two hospitals in Wuhan and who underwent serial chest CT scans were retrospectively enrolled. Patients were grouped on the basis of the interval between symptom onset and the first CT scan: group 1 (subclinical patients; scans done before symptom onset), group 2 (scans done ≤1 week after symptom onset), group 3 (>1 week to 2 weeks), and group 4 (>2 weeks to 3 weeks). Imaging features and their distribution were analysed and compared across the four groups.
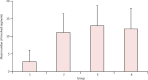
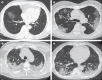
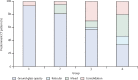
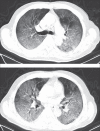
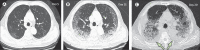
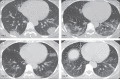
Findings: 81 patients admitted to hospital between Dec 20, 2019, and Jan 23, 2020, were retrospectively enrolled. The cohort included 42 (52%) men and 39 (48%) women, and the mean age was 49·5 years (SD 11·0). The mean number of involved lung segments was 10·5 (SD 6·4) overall, 2·8 (3·3) in group 1, 11·1 (5·4) in group 2, 13·0 (5·7) in group 3, and 12·1 (5·9) in group 4. The predominant pattern of abnormality observed was bilateral (64 [79%] patients), peripheral (44 [54%]), ill-defined (66 [81%]), and ground-glass opacification (53 [65%]), mainly involving the right lower lobes (225 [27%] of 849 affected segments). In group 1 (n=15), the predominant pattern was unilateral (nine [60%]) and multifocal (eight [53%]) ground-glass opacities (14 [93%]). Lesions quickly evolved to bilateral (19 [90%]), diffuse (11 [52%]) ground-glass opacity predominance (17 [81%]) in group 2 (n=21). Thereafter, the prevalence of ground-glass opacities continued to decrease (17 [57%] of 30 patients in group 3, and five [33%] of 15 in group 4), and consolidation and mixed patterns became more frequent (12 [40%] in group 3, eight [53%] in group 4).
Interpretation: COVID-19 pneumonia manifests with chest CT imaging abnormalities, even in asymptomatic patients, with rapid evolution from focal unilateral to diffuse bilateral ground-glass opacities that progressed to or co-existed with consolidations within 1-3 weeks. Combining assessment of imaging features with clinical and laboratory findings could facilitate early diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia.
Funding: None.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
COVID-19 pneumonia: what has CT taught us?Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Apr;20(4):384-385. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30134-1. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32105641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
CT screening for early diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection - Authors' reply.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Sep;20(9):1011. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30247-4. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32222163 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
CT screening for early diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Sep;20(9):1010-1011. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30241-3. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32222164 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
CT Manifestation of COVID-19 Pneumonia; Role of Multiplanar Imaging.Acad Radiol. 2020 May;27(5):753-754. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.03.028. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Acad Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32276754 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO Novel coronavirus—China. Jan 12, 2020. https://www.who.int/csr/don/12-january-2020-novel-coronavirus-china/en/
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

