Neural correlates of symptom severity in obsessive-compulsive disorder using magnetization transfer and diffusion tensor imaging
- PMID: 32106018
- PMCID: PMC7100004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2020.111046
Neural correlates of symptom severity in obsessive-compulsive disorder using magnetization transfer and diffusion tensor imaging
Abstract
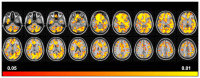
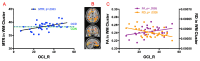
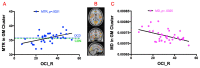
Recent neuroimaging studies in OCD have reported structural alterations in the brain, not limited to frontostriatal regions. While Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) is typically used to interrogate WM microstructure in OCD, additional imaging metric, such as Magnetization Transfer Imaging (MTI), allows for further identification of subtle but important structural changes across both GM and WM. In this study, both MTI and DTI were utilised to investigate the structural integrity of the brain, in OCD in relation to healthy controls. 38 adult OCD patients were recruited, along with 41 age- and gender-matched controls. Structural T1, MTI and DTI data were collected. Case-control differences in Magnetization Transfer Ratio (MTR) and DTI metrics (FA, MD) were examined, along with MTR/DTI-related associations with symptom severity in patients. No significant group differences were found across MTR, FA, and MD. However, OCD symptom severity was positively correlated with MTR in a distributed network of brain regions, including the striatum, cingulate, orbitofrontal area and insula. Within the same regions, OCD symptoms were also positively correlated with FA in WM, and negatively correlated with MD in GM. These results indicate a greater degree of myelination in certain cortical and subcortical regions in the more severe cases of OCD.
Keywords: DTI; Diffusion tensor imaging; MTI; Magnetization transfer imaging; OCD; Obsessive-Compulsive disorder.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cortical thickness and white matter integrity abnormalities in obsessive-compulsive disorder: A combined multimodal surface-based morphometry and tract-based spatial statistics study.Depress Anxiety. 2018 Aug;35(8):742-751. doi: 10.1002/da.22758. Epub 2018 May 7. Depress Anxiety. 2018. PMID: 29734487
-
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is a heterogeneous disorder: evidence from diffusion tensor imaging and magnetization transfer imaging.BMC Psychiatry. 2015 Jun 25;15:135. doi: 10.1186/s12888-015-0535-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26109055 Free PMC article.
-
Microstructural brain abnormalities and symptom dimensions in child and adolescent patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study.Depress Anxiety. 2014 Dec;31(12):1007-17. doi: 10.1002/da.22330. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Depress Anxiety. 2014. PMID: 25450164
-
Advances in DTI studies for diagnoses and treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder.Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2024 Jun;340:111794. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2024.111794. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2024. PMID: 38422871 Review.
-
Reduced focal fiber collinearity in the cingulum bundle in adults with obsessive-compulsive disorder.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Jun;44(7):1182-1188. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0353-4. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30802896 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between gray/white matter contrast and white matter microstructural alterations in medication-naïve obsessive-compulsive disorder.Neuroimage Clin. 2022;35:103122. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103122. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Neuroimage Clin. 2022. PMID: 35872436 Free PMC article.
-
Application of advanced magnetic resonance imaging in glaucoma: a narrative review.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022 Mar;12(3):2106-2128. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-790. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022. PMID: 35284278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative myelin imaging with MRI and PET: an overview of techniques and their validation status.Brain. 2023 Apr 19;146(4):1243-1266. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac436. Brain. 2023. PMID: 36408715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in white matter microstructure in the brain of patients with inflammatory bowel disease are associated with abdominal pain.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jul 8;19:1570425. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1570425. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40697271 Free PMC article.
-
Individuals with problem gambling and obsessive-compulsive disorder learn through distinct reinforcement mechanisms.PLoS Biol. 2023 Mar 14;21(3):e3002031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002031. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 36917567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramowitz JS, Deacon BJ, Olatunji BO, Wheaton MG, Berman NC, Losardo D, Timpano KR, McGrath PB, Riemann BC, Adams T, Björgvinsson T, et al. Assessment of Obsessive-Compulsive Symptom Dimensions: Development and Evaluation of the Dimensional Obsessive-Compulsive Scale. Psychol Assess. 2010;22:180–98. doi: 10.1037/a0018260. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexander AL, Hurley SA, Samsonov AA, Adluru N, Pasha A, Mossahebi P, Tromp DPM, Zakszewski E, Field AS, Hosseinbor AP, Mossahebi P, et al. Characterization of cerebral white matter properties using quantitative magnetic resonance imaging stains. Brain Connect. 2011;1:423–46. doi: 10.1089/brain.2011.0071.Characterization. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anticevic A, Hu S, Zhang S, Savic A, Billingslea E, Wasylink S, Repovs G, Cole MW, Bednarski S, Krystal JH, Bloch MH, et al. Global resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging analysis identifies frontal cortex, striatal, and cerebellar dysconnectivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;75:595–605. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.10.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- APA. American Journal of Psychiatry. 5th ed. 2013. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

