Multidrug-Resistant ESBL/AmpC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Healthy Thoroughbred Racehorses in Japan
- PMID: 32106501
- PMCID: PMC7143125
- DOI: 10.3390/ani10030369
Multidrug-Resistant ESBL/AmpC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Healthy Thoroughbred Racehorses in Japan
Abstract
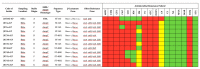
Extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)- and AmpC β-lactamase (AmpC)-producing Klebsiella spp. have become a major health problem, leading to treatment failure in humans and animals. This study aimed to evaluate the presence of ESBL/AmpC-producing Klebsiella spp. isolated from racehorses in Japan. Feces samples from 212 healthy Thoroughbred racehorses were collected from the Japan Racing Association Training Centers between March 2017 and August 2018. ESBL/AmpC-producing Klebsiella spp. were isolated using selective medium containing 1 µg/mL cefotaxime. All isolates were subjected to bacterial species identification (MALDI-TOF MS), antimicrobial susceptibility test (disk diffusion test), characterization of resistance genes (PCR), conjugation assay, and genetic relatedness (multilocus sequence typing/MLST). Twelve ESBL/AmpC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL/AmpC-KP) were isolated from 3.3% of horse samples. Antimicrobial resistance profiling for 17 antimicrobials showed all ESBL/AmpC-KP were multidrug-resistant (MDR). Only 1 isolate was confirmed as an ESBL producer (blaCTX-M-2-positive), whereas the other 11 isolates were plasmid-mediated AmpC (pAmpC) producers (blaCMY positive). On the basis of MLST analysis, the ESBL-KP isolate was identified as sequence type (ST)-133 and four different STs among AmpC-KP isolates, ST-145, ST-4830, ST-4831, and ST-4832, were found to share six of the seven loci constituting a single-locus variant. This is the first study to show K. pneumoniae carrying MDR pAmpC isolated from a racehorse.
Keywords: AmpC β-lactamase; Klebsiella pneumoniae; extended-spectrum β-lactamase; horse; multidrug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Trigo da Roza F., Couto N., Carneiro C., Cunha E., Rosa T., Magalhães M., Tavares L., Novais Â., Peixe L., Rossen J.W., et al. Commonality of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST348 isolates in horses and humans in Portugal. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:1657. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01657. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Donati V., Feltrin F., Hendriksen R.S., Svendsen C.A., Cordaro G., García-Fernández A., Lorenzetti S., Lorenzetti R., Battisti A., Franco A. Extended-spectrum-beta-lactamases, AmpC beta-lactamases and plasmid mediated quinolone resistance in Klebsiella spp. from companion animals in Italy. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e90564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090564. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Satué K., Gardon J.C. Infection and infertility in mares. In: Darwish A., editor. Genital Infections and Infertility. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2016. [(accessed on 10 February 2020)]. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/genital-infections-and-infertility/infe....
-
- Lam M.M.C., Wyres K.L., Duchêne S., Wick R.R., Judd L.M., Gan Y.H., Hoh C.H., Archuleta S., Molton J.S., Kalimuddin S., et al. Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal-group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:2703. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05114-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

