Effectiveness of a clinic-based randomized controlled intervention for type 2 diabetes management: an innovative model of intensified diabetes management in Mainland China (C-IDM study)
- PMID: 32107265
- PMCID: PMC7206907
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-001030
Effectiveness of a clinic-based randomized controlled intervention for type 2 diabetes management: an innovative model of intensified diabetes management in Mainland China (C-IDM study)
Abstract
Objectives: Highly efficient diabetes management programs are needed for tackling diabetes in China. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of a clinic-based intensified diabetes management model (C-IDM) in Mainland China.
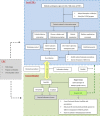
Research design and methods: A 2-year clinic-based randomized controlled trial was conducted among patients with type 2 diabetes in Nanjing, China. The C-IDM intervention components comprised four domains (disease targeting management, express referral channel, expert visit, patients' self-management) and an integrated running system (disease control centers, general hospitals and local clinics). Control group participants received their usual care, while intervention participants received both the C-IDM package and the usual services. The primary outcome variable was change of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). Mixed-effects models were used to compute effect estimates and 95% CI with consideration of both individual and cluster-level confounders.
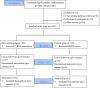
Results: Overall, 1095 of 1143 participants were assessed at study completion. The mean change in HbA1c was significantly greater in the intervention group than in the control group (mean difference (MD)=-0.57, 95% CI -0.79 to -0.36). Similar results were observed for change in body mass index (MD=-0.29, 95% CI -0.49 to -0.10). Participants in the intervention group were more likely to achieve normal HbA1c and body weight compared with their counterparts in control group after adjusting for potentially confounding variables (adjusted OR=1.94, 95% CI 1.35 to 2.81 and 1.79, 95% CI 1.13 to 2.85, respectively).
Conclusions: The C-IDM model is feasible and effective in large-scale management of patients with type 2 diabetes in China. It has public health implications for tackling the burden of diabetes in China.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR-IOR-15006019.
Keywords: China; clinic-based; diabetes care; intervention; management model.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Pan X. Strive to prevent and control diabetes in China. Chin Med J 1995;108:83–5. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, McGreevey WP, Fu C, et al. . Type 2 diabetes mellitus in China: a preventable economic burden. Am J Manag Care 2009;15:593–601. - PubMed
-
- Qin H, Chen B. National technical specifications for basic public health services. Bejing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
