Comparison of iRECIST versus RECIST V.1.1 in patients treated with an anti-PD-1 or PD-L1 antibody: pooled FDA analysis
- PMID: 32107275
- PMCID: PMC7057528
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000146
Comparison of iRECIST versus RECIST V.1.1 in patients treated with an anti-PD-1 or PD-L1 antibody: pooled FDA analysis
Abstract
Background: Response criteria developed when cytotoxic chemotherapy was the predominant therapeutic modality to treat patients with cancer, do not capture the full spectrum of tumor response patterns observed with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody treatment. iRECIST was developed to capture both typical and atypical response patterns.
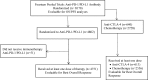
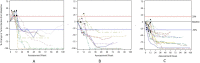
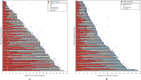
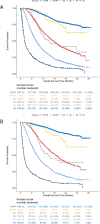
Methods: Target, non-target, and new lesion measurements for 7920 patients receiving anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody (n=4751) or anti-CTLA-4 antibody (n=613) or undergoing chemotherapy (n=2556) from 14 randomized controlled trials submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration were used to calculate the best overall response, objective response rate and progression-free survival (PFS) per iRECIST (iPFS) and Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours (RECIST). Associations between either PFS or iPFS and overall survival (OS) were evaluated using the method adopted by Oba et al.1 RESULTS: Among 4751 anti-PD-1/PD-L1-antibody treated patients, 31.5% (95% CI 30.2% to 32.9%) and 30.5% (95% CI 29.2% to 31.8%) achieved an objective response per iRECIST or RECIST V.1.1, respectively. OS among the 48 patients with objective response by iRECIST only resembled that in patients with responses per RECIST V.1.1. The association between iPFS and OS was R2=0.277 and that between PFS and OS was R2=0.260.
Conclusions: Patients treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies with initial progressive disease per RECIST V.1.1 can experience prolonged stability or substantial reductions in tumor burden per iRECIST, atypical response patterns associated with prolonged OS. In the subgroup of patients with atypical responses, the application of iRECIST retrospectively in the evaluation of the objective response durations and the magnitude of PFS results in large differences compared with RECIST V.1.1. For the overall pooled population, the magnitude of these differences was modest, although a large proportion of patients had no further tumor assessments following RECIST V.1.1-defined progressive disease. Prospective studies employing iRECIST will be required to assess whether this response criteria more fully captures the benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Keywords: oncology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- FDA Clinical trial endpoints for the approval of cancer drugs and biologics guidance for industry 2018.
-
- Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et al. . New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European organization for research and treatment of cancer, National cancer Institute of the United States, National cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000;92:205–16.10.1093/jnci/92.3.205 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
