Common transcriptional signatures of neuropathic pain
- PMID: 32107361
- PMCID: PMC7302324
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001847
Common transcriptional signatures of neuropathic pain
Abstract
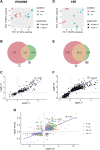
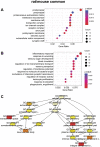
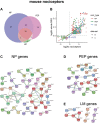
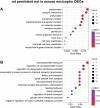
The dorsal root ganglia (DRG) are key structures in nociception and chronic pain disorders. Several gene expression studies of DRG in preclinical pain models have been performed, but it is unclear if consistent gene changes are identifiable. We, therefore, compared several recent RNA-Seq data sets on the whole DRG in rodent models of nerve injury. Contrary to previous findings, we show hundreds of common differentially expressed genes and high positive correlation between studies, despite model and species differences. We also find, in contrast to previous studies, that 60% of the common rodent gene response after injury is likely to occur in nociceptors of the DRG. Substantial expression changes are observed at a 1-week time-point, with smaller changes in the same genes at a later 3- to 4-week time-point. However, a subset of genes shows a similar magnitude of changes at both early and late time-points, suggesting their potential involvement in the maintenance of chronic pain. These genes are centred around suppression of endogenous opioid signalling. Reversal of this suppression could allow endogenous and exogenous opioids to exert their analgesic functions and may be an important strategy for treating chronic pain disorders. Currently used drugs, such as amitriptyline and duloxetine, do not seem to appropriately modulate many of the critical pain genes and indeed may transcriptionally suppress endogenous opioid signalling further.
Conflict of interest statement
M.Z. Cader has received honoraria from Novartis, TEVA, Orion, and Eli Lilly. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
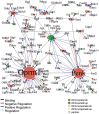
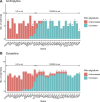
References
-
- Alexa A, Rahnenfuhrer J, Lengauer T. Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure. Bioinformatics 2006;22:1600–7. - PubMed
-
- Arner S, Meyerson BA. Lack of analgesic effect of opioids on neuropathic and idiopathic forms of pain. PAIN 1988;33:11–23. - PubMed
-
- Bangash MA, Alles SRA, Santana-Varela S, Millet Q, Sikandar S, de Clauser L, Ter Heegde F, Habib AM, Pereira V, Sexton JE, Emery EC, Li S, Luiz AP, Erdos J, Gossage SJ, Zhao J, Cox JJ, Wood JN. Distinct transcriptional responses of mouse sensory neurons in models of human chronic pain conditions. Wellcome Open Res 2018;3:78. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baskozos G, Dawes JM, Austin JS, Antunes-Martins A, McDermott L, Clark AJ, Trendafilova T, Lees JG, McMahon SB, Mogil JS, Orengo C, Bennett DL. Comprehensive analysis of long noncoding RNA expression in dorsal root ganglion reveals cell-type specificity and dysregulation after nerve injury. PAIN 2019;160:463–85. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

