Clonal Relationship Between Lichen Sclerosus, Differentiated Vulvar Intra-epithelial Neoplasia and Non HPV-related Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 32108037
- PMCID: PMC7078831
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20175
Clonal Relationship Between Lichen Sclerosus, Differentiated Vulvar Intra-epithelial Neoplasia and Non HPV-related Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background/aim: Differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (dVIN) and lichen sclerosus (LS) can give rise to vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (VSCC), but genetic evidence is currently still limited. We aimed to determine genetic abnormalities in VSCC and backtrack these abnormalities in the dVIN and LS lesions.
Materials and methods: DNA from VSCC and patient-matched dVIN and LS samples of twelve patients was collected. High-resolution genome-wide copy number analysis was performed and subsequently, we sequenced TP53.
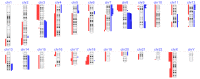
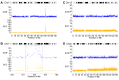
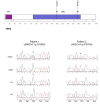
Results: Copy number alterations were identified in all VSCC samples. One dVIN lesion presented with three copy number alterations that were preserved in the paired VSCC sample. Targeted sequencing of TP53 identified mutations in five VSCCs. All five mutations were traced back in the dVIN (n=5) or the LS (n=1) with frequencies ranging from 3-19%.
Conclusion: Our data provide genetic evidence for a clonal relationship between VSCC and dVIN or LS.
Keywords: Vulvar cancer; clonal evolution; differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia; lichen sclerosus; squamous cell carcinoma; vulvar lichen sclerosus; vulvar neoplasms.
Copyright© 2020, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Schuurman MS, van den Einden LC, Massuger LF, Kiemeney LA, van der Aa MA, de Hullu JA. Trends in incidence and survival of dutch women with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(18):3872–3880. PMID: 24011936. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.08.003. - PubMed
-
- van der Avoort IA, Shirango H, Hoevenaars BM, Grefte JM, de Hullu JA, de Wilde PC, Bulten J, Melchers WJ, Massuger LF. Vulvar squamous cell carcinoma is a multifactorial disease following two separate and independent pathways. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2006;25(1):22–29. PMID: 16306780. DOI: 10.1097/01.pgp.0000177646.38266.6a. - PubMed
-
- Hoevenaars BM, van der Avoort IA, de Wilde PC, Massuger LF, Melchers WJ, de Hullu JA, Bulten J. A panel of p16(ink4a), mib1 and p53 proteins can distinguish between the 2 pathways leading to vulvar squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2008;123(12):2767–2773. PMID: 18798277. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.23857. - PubMed
-
- van de Nieuwenhof HP, van Kempen LC, de Hullu JA, Bekkers RL, Bulten J, Melchers WJ, Massuger LF. The etiologic role of hpv in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma fine tuned. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18(7):2061–2067. PMID: 19567503. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.epi-09-0209. - PubMed
-
- de Sanjose S, Alemany L, Ordi J, Tous S, Alejo M, Bigby SM, Joura EA, Maldonado P, Laco J, Bravo IG, Vidal A, Guimera N, Cross P, Wain GV, Petry KU, Mariani L, Bergeron C, Mandys V, Sica AR, Felix A, Usubutun A, Seoud M, Hernandez-Suarez G, Nowakowski AM, Wilson G, Dalstein V, Hampl M, Kasamatsu ES, Lombardi LE, Tinoco L, Alvarado-Cabrero I, Perrotta M, Bhatla N, Agorastos T, Lynch CF, Goodman MT, Shin HR, Viarheichyk H, Jach R, Cruz MO, Velasco J, Molina C, Bornstein J, Ferrera A, Domingo EJ, Chou CY, Banjo AF, Castellsague X, Pawlita M, Lloveras B, Quint WG, Munoz N, Bosch FX, group HVs. Worldwide human papillomavirus genotype attribution in over 2000 cases of intraepithelial and invasive lesions of the vulva. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(16):3450–3461. PMID: 23886586. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.06.033. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
