Crossing Boundaries: Steps Toward Measuring Undergraduates' Interdisciplinary Science Understanding
- PMID: 32108558
- PMCID: PMC8697648
- DOI: 10.1187/cbe.19-09-0168
Crossing Boundaries: Steps Toward Measuring Undergraduates' Interdisciplinary Science Understanding
Abstract
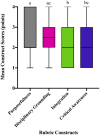
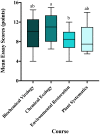
A desired outcome of education reform efforts is for undergraduates to effectively integrate knowledge across disciplines in order to evaluate and address real-world issues. Yet there are few assessments designed to measure if and how students think interdisciplinarily. Here, a sample of science faculty were surveyed to understand how they currently assess students' interdisciplinary science understanding. Results indicate that individual writing-intensive activities are the most frequently used assessment type (69%). To understand how writing assignments can accurately assess students' ability to think interdisciplinarily, we used a preexisting rubric, designed to measure social science students' interdisciplinary understanding, to assess writing assignments from 71 undergraduate science students. Semistructured interviews were conducted with 25 of those students to explore similarities and differences between assignment scores and verbal understanding of interdisciplinary science. Results suggest that certain constructs of the instrument did not fully capture this competency for our population, but instead, an interdisciplinary framework may be a better model to guide assessment development of interdisciplinary science. These data suggest that a new instrument designed through the lens of this model could more accurately characterize interdisciplinary science understanding for undergraduate students.
Figures


References
-
- American Association for the Advancement of Science. (2011). Vision and change: A call to action. Final report. Washington, DC. Retrieved July 22, 2019, from http://visionandchange.org/finalreport
-
- American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education. (2013). Standards for educational and psychological testing. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association.
-
- Balgopal, M. M., Wallace, A. M. (2009). Decisions and dilemmas: Using writing to learn activities to increase ecological literacy. Journal of Environmental Education, 40(3), 13–26.
-
- Balgopal, M. M., Wallace, A. M., Dahlberg, S. (2012). Writing to learn ecology: A study of three populations of college students. Environmental Education Research, 18(1), 67–90.
-
- Balgopal, M. M., Wallace, A. M., Dahlberg, S. (2017). Writing from different cultural contexts: How college students frame an environmental SSI through written arguments. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 54(2), 195–218.

