Estimation of the Number of Brazilian Women Living With Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 32109156
- PMCID: PMC7051793
- DOI: 10.1200/JGO.19.00404
Estimation of the Number of Brazilian Women Living With Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer is the most common cancer and the leading cause of cancer-related death in women worldwide. The number of women living with metastatic breast cancer (MBC) in Brazil is unknown. The objective of this article was to use population-based data to estimate the prevalence of MBC in Brazil.
Methods: Using 4 different sources and cancer registries (DataSUS, Registro Hospitalar de Câncer, the Brazilian National Health Agency, and the National Geography and Statistics Institute) with data from 2008 to 2018, we built a database that represents Brazilian MBC cases. The current number of women in the model living with MBC was considered the prevalence (recurrent or de novo), and new cases in the year 2018 represented the incidence. In each of these outcomes, we were able to separate our population on the basis of cancer subtype, age, and time from diagnosis.
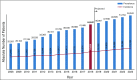
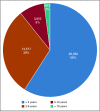
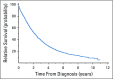
Results: We estimate that 44,642 women currently live with MBC in Brazil. This accounts for one in every 2,409 Brazilian women and approximately 41 women per 100,000. A total of 58% have hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative tumors, 25% are human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive, and 16% have triple-negative breast cancer. According to our methodology, the estimated median overall survival of Brazilian women after diagnosis of MBC is 26.2 months.
Conclusion: The significant number of patients living with MBC should inform and raise the interest of the many stakeholders involved. This collaborative effort is a clear requirement to improve the lives of these patients as well as to prepare for future challenges related to the trend of a progressive increase in MBC prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
Tomás Reinert
Rodrigo Rol
Carlos Henrique Barrios
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures



References
-
- Goss PE, Lee BL, Badovinac-Crnjevic T, et al. Planning cancer control in Latin America and the Caribbean. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:391–436. - PubMed
-
- Booth CM, Karim S, Mackillop WJ. Real-world data: Towards achieving the achievable in cancer care. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16:312–325. - PubMed
-
- Departamento de Informática do Sistema Único de Saúde: http://datasus.saude.gov.br/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

