Diagnosis and Treatment of Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis (hATTR) Polyneuropathy: Current Perspectives on Improving Patient Care
- PMID: 32110029
- PMCID: PMC7041433
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S219979
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis (hATTR) Polyneuropathy: Current Perspectives on Improving Patient Care
Abstract
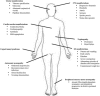
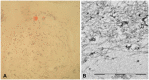
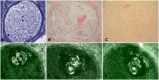
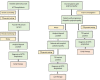
Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis (hATTR) with polyneuropathy (formerly known as Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy) is a rare disease due to mutations in the gene encoding transthyretin (TTR) and characterized by multisystem extracellular deposition of amyloid, leading to dysfunction of different organs and tissues. hATTR amyloidosis represents a diagnostic challenge for neurologists considering the great variability in clinical presentation and multiorgan involvement. Generally, patients present with polyneuropathy, but clinicians should consider the frequent cardiac, ocular and renal impairment. Especially a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, even if usually latent, is identifiable in at least 50% of the patients. Therapeutically, current available options act at different stages of TTR production, including synthesis inhibition (liver transplantation and/or gene-silencing drugs) or tetramer TTR stabilization (TTR stabilizers), increasing survival at different disease stages.
Keywords: amyloid; clinical care; polyneuropathy; therapy; transthyretin.
© 2020 Luigetti et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Luigetti received financial grants (honoraria and speaking) from Akcea, Alnylam and Pfizer, and travel grants from Pfizer, Kedrion and Grifols; Dr Bisogni received financial grants (honoraria and speaking) from Alnylam, and travel grants from Pfizer, and Grifols; Dr Romano received travel grants from Akcea and Pfizer; Dr Di Paolantonio received travel grants from Akcea and Pfizer; Dr Sabatelli received financial grants (honoraria and speaking) from Akcea. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

