Plasma metabolomic profile in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 32110382
- PMCID: PMC7000865
- DOI: 10.1177/2045894019890553
Plasma metabolomic profile in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
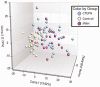
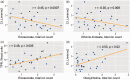
We aimed to characterize the plasma metabolome of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients using a high-throughput unbiased omics approach. We collected fasting plasma from a peripheral vein in 33 operable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients, 31 healthy controls, and 21 idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension patients matched for age, gender, and body mass index. Metabolomic analysis was performed using an untargeted approach (Metabolon Inc. Durham, NC). Of the total of 862 metabolites identified, 362 were different in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension compared to controls: 178 were higher and 184 were lower. Compared to idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension, 147 metabolites were different in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: 45 were higher and 102 were lower. The plasma metabolome allowed us to distinguish subjects with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and healthy controls with a predictive accuracy of 89%, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension versus idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension with 80% accuracy. Compared to idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension and healthy controls, chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients had higher fatty acids and glycerol; while acyl cholines and lysophospholipids were lower. Compared to healthy controls, both idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients had increased acyl carnitines, beta-hydroxybutyrate, amino sugars and modified amino acids and nucleosides. The plasma global metabolomic profile of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension suggests aberrant lipid metabolism characterized by increased lipolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and ketogenesis, concomitant with reduced acyl choline and phospholipid moieties. Future research should investigate the pathogenetic and therapeutic potential of modulating lipid metabolism in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.
Keywords: chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; ketogenesis; lipolysis; metabolism.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Figures

References
-
- Moser KM, Bloor CM. Pulmonary vascular lesions occurring in patients with chronic major vessel thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Chest 1993; 103: 685–692. - PubMed
-
- Dorfmuller P, Gunther S, Ghigna MR, et al. Microvascular disease in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a role for pulmonary veins and systemic vasculature. Eur Respir J 2014; 44: 1275–1288. - PubMed
-
- Dorfmuller P, Humbert M, Perros F, et al. Fibrous remodeling of the pulmonary venous system in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue diseases. Hum Pathol 2007; 38: 893–902. - PubMed
-
- Paulin R, Michelakis ED. The metabolic theory of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ Res 2014; 115: 148–164. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

