Sustained drug retention after paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty for superficial femoral artery disease: Follow-up intravascular imaging
- PMID: 32110413
- PMCID: PMC7026811
- DOI: 10.1177/2050313X20907825
Sustained drug retention after paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty for superficial femoral artery disease: Follow-up intravascular imaging
Abstract
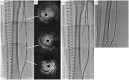
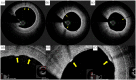
A 63 year-old woman with claudication underwent endovascular therapy for diffuse stenosis of the right superficial femoral artery in our hospital. We performed paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty using the IN.PACT™ Admiral™ and achieved acceptable results. After 42 days, we performed follow-up optical frequency domain imaging for the right superficial femoral artery lesion treated with paclitaxel-coated balloon and observed several high-intensity regions with attenuation on the lumen surface. Sustained drug availability is a notable characteristic of paclitaxel-coated balloon. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the visualization of sustained drug retention on the lumen surface using follow-up optical frequency domain imaging after paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty in a human patient with superficial femoral artery disease.
Keywords: Paclitaxel-coated balloon; optical coherence tomography; optical frequency domain imaging; superficial femoral artery disease.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mortality Not Correlated With Paclitaxel Exposure: An Independent Patient-Level Meta-Analysis of a Drug-Coated Balloon.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 May 28;73(20):2550-2563. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Jan 25. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30690141 Review.
-
Revascularization of the superficial femoral artery with paclitaxel-coated balloon for claudication.Acta Chir Belg. 2018 Feb;118(1):42-47. doi: 10.1080/00015458.2017.1374593. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Acta Chir Belg. 2018. PMID: 28891401
-
Mortality After Paclitaxel Coated Balloon Angioplasty and Stenting of Superficial Femoral and Popliteal Artery in the Vascular Quality Initiative.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Feb;13(2):e008528. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.119.008528. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2020. PMID: 32069110
-
Serial Morphological and Functional Assessment of the Paclitaxel-coated Balloon for de Novo Lesions.Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2016 Nov;69(11):1026-1032. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2016.03.026. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2016. PMID: 27321644 English, Spanish.
-
IN.PACT™ Admiral™ drug-coated balloon: Durable, consistent and safe treatment for femoropopliteal peripheral artery disease.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017 Mar;112:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017. PMID: 27771367 Review.
Cited by
-
Difference in one-year late lumen loss between high- and low-dose paclitaxel-coated balloons for femoropopliteal disease.Heart Vessels. 2024 Jul;39(7):582-588. doi: 10.1007/s00380-024-02370-0. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Heart Vessels. 2024. PMID: 38363331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laird JR, Schneider PA, Tepe G, et al. Durability of treatment effect using a drug-coated balloon for femoropopliteal lesions: 24-month results of IN.PACT SFA. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 66(21): 2329–2338. - PubMed
-
- Mirzapoiazova T, Kolosova IA, Moreno L, et al. Suppression of endotoxin-induced inflammation by taxol. Eur Respir J 2007; 30(3): 429–435. - PubMed
-
- Gongora CA, Shibuya M, Wessler JD, et al. Impact of paclitaxel dose on tissue pharmacokinetics and vascular healing: a comparative drug-coated balloon study in the familial hypercholesterolemic swine model of superficial femoral in-stent restenosis. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2015; 8(8): 1115–1123. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto T, Itoh T, Shimoda Y, et al. OCT visualization of the structure of intimal tissue after drug-eluting balloon deployment. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2015; 8(8): 983–984. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

