Precision medicine in the diagnosis and treatment of male lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 32110513
- PMCID: PMC7015008
- DOI: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_107_19
Precision medicine in the diagnosis and treatment of male lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
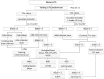
Male lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTSs) are highly prevalent in men and the incidence increases with aging. The pathophysiology of male LUTSs might be bladder outlet dysfunctions such as bladder neck (BN) dysfunction, benign prostatic obstruction, and poor relaxation of external sphincter and bladder dysfunctions such as detrusor overactivity (DO), detrusor underactivity, DO, and inadequate contractility. Male LUTSs include voiding and storage symptoms, and precision diagnosis should not be done based on the symptoms alone. Videourodynamic study provides a thorough look at the bladder and bladder outlet and can clearly demonstrate the underlying pathophysiology when the initial medication fails to relieve LUTS. Medical treatment should be given based on the underlying pathophysiology of LUTS, and surgical intervention to remove prostate should only be performed when a definite bladder outlet obstruction due to prostatic obstruction has been confirmed by invasive urodynamic study.
Keywords: Benign prostatic hyperplasia; Bladder outlet obstruction; Lower urinary tract symptoms; Overactive bladder; Voiding dysfunction.
Copyright: © 2019 Tzu Chi Medical Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Videourodynamic analysis of pathophysiology of men with both storage and voiding lower urinary tract symptoms.Urology. 2007 Aug;70(2):272-6. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.03.063. Urology. 2007. PMID: 17826488
-
Role of videourodynamic study in precision diagnosis and treatment for lower urinary tract dysfunction.Tzu Chi Med J. 2019 Nov 18;32(2):121-130. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_178_19. eCollection 2020 Apr-Jun. Tzu Chi Med J. 2019. PMID: 32269943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Videourodynamic findings of lower urinary tract dysfunctions in men with persistent storage lower urinary tract symptoms after medical treatment.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 20;13(2):e0190704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190704. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29462145 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of tadalafil on storage and voiding function in patients with male lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia: A urodynamic-based study.Int J Urol. 2018 Mar;25(3):246-250. doi: 10.1111/iju.13489. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Int J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29164680 Clinical Trial.
-
Recent research on the role of urodynamic study in the diagnosis and treatment of male lower urinary tract symptoms and urinary incontinence.Tzu Chi Med J. 2017 Apr-Jun;29(2):72-78. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_19_17. Tzu Chi Med J. 2017. PMID: 28757770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of urine microbiota in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021 Apr 15;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12941-021-00428-9. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021. PMID: 33858430 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotyping Men With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Results From the Symptoms of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Research Network.Neurourol Urodyn. 2025 Jan;44(1):178-193. doi: 10.1002/nau.25596. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Neurourol Urodyn. 2025. PMID: 39370868 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Urethral Contrast Computed Tomography Three-Dimensional Imaging in the Postoperative Assessment of Prostate Hyperplasia.Am J Mens Health. 2024 May-Jun;18(3):15579883241258319. doi: 10.1177/15579883241258319. Am J Mens Health. 2024. PMID: 38864148 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of red ginseng oil(KGC11o) on testosterone-propionate-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia.J Ginseng Res. 2022 May;46(3):473-480. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Nov 13. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 35600774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barry MJ, Fowler FJ, Jr, O'Leary MP, Bruskewitz RC, Holtgrewe HL, Mebust WK, et al. The American Urological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The measurement committee of the American Urological Association. J Urol. 1992;148:1549–57. - PubMed
-
- Milsom I, Abrams P, Cardozo L, Roberts RG, Thüroff J, Wein AJ. How widespread are the symptoms of an overactive bladder and how are they managed? A population-based prevalence study. BJU Int. 2001;87:760–6. - PubMed
-
- Eckhardt MD, van Venrooij GE, Boon TA. Symptoms, prostate volume, and urodynamic findings in elderly male volunteers without and with LUTS and in patients with LUTS suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2001;58:966–71. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, Li YW, Wu WR, Lu Q. Long-term clinical efficacy and safety profile of transurethral resection of prostate versus plasmakinetic resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2017;103:198–203. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
