Antibacterial activity of Syzygium aromaticum (clove) against uropathogens producing ESBL, MBL, and AmpC beta-lactamase: Are we close to getting a new antibacterial agent?
- PMID: 32110587
- PMCID: PMC7014883
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_908_19
Antibacterial activity of Syzygium aromaticum (clove) against uropathogens producing ESBL, MBL, and AmpC beta-lactamase: Are we close to getting a new antibacterial agent?
Abstract
Introduction: The present study was done to access the antibacterial activity of clove (Syzygium aromaticum) against extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL), metallo-beta-lactamase (MBL), and AmpC beta-lactamase-producing gram-negative bacteria causing urinary tract infection.
Methods: A total of 221 gram-negative uropathogens were isolated and screened for beta-lactamase (ESBL, MBL, and AmpC) production and further tested against ethanolic extract of clove (S. aromaticum) for its antibacterial activity.
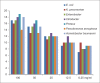
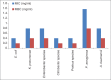
Results: Clove was effective against all gram-negative isolates but the best antibacterial activity was shown against Proteus species with 19 mm zone of inhibition, 0.39 mg/ml minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and 0.19 mg/ml minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC).
Conclusions: Clove extract showed different antibacterial potential against all gram-negative uropathogens. Clove activity for particular strain was found to be similar between isolates producing beta-lactamase and non beta-lactamase.
Keywords: Extended-spectrum β-lactamases; Syzygium aromaticum (clove); and AmpC beta-lactamase; metallo-beta-lactamase; urinary tract infection; uropathogens.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Moroh J-LA, Fleury Y, Tia H, Bahi C, Lietard C, Coroller L, et al. Diversity and antibiotic resistance of uropathogenic bacteria from Abidjan. Afr J Urol. 2014;20:18–24.
-
- Farajnia S, Alikhani MY, Ghotaslou R, Naghili B, Nakhlband A. Causative agents and antimicrobial susceptibilities of urinary tract infections in the northwest of Iran. Int J Infect Dis. 2009;13:140–4. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad I, Beg AZ. Antimicrobial and phytochemical studies on 45 Indian medicinal plants against multi-drug resistant human pathogens. J Ethnopharmacol. 2001;74:113–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous