Efficacy of remineralizing agents to occlude dentinal tubules in primary teeth subjected to dentin hypersensitivity in vitro: SEM study
- PMID: 32110618
- PMCID: PMC7014855
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_853_19
Efficacy of remineralizing agents to occlude dentinal tubules in primary teeth subjected to dentin hypersensitivity in vitro: SEM study
Abstract
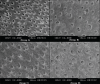
Aim: Comparison of casein phosphopeptides (CPPs) and amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP), tricalcium phosphate, and hydroxyapatite on assessment of dentine tubule occlusion on primary enamel using scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Materials and methods: A total of 20 freshly extracted noncarious primary molars were randomly divided into four groups (A to D) with five sections in each group; group A: negative control, group B: CPP-ACP, group C: tricalcium phosphate, and group D: Hydroxyapatite (HA). To assess tubule occlusion, 20 dentin sections of 2 mm thickness were obtained from cervical third of sound primary molars. Each section were processed to simulate the hypersensitive dentin and the test agents were brushed over the sections with an electric toothbrush and observed under SEM for calculation of the percentage of occluded tubules.
Results: Group B and D showed greater percentage of tubule occlusion than group C. Intergroup comparison of tubule occlusion potential of Group B and D was not significant.
Conclusion: HA showed significantly higher dentinal tubule occlusion when compared to CPP-ACP and tricalcium phosphate.
Keywords: CPP-ACP; dentinal hypersensitivity; hydroxyapatite; scanning electron microscope; tricalcium phosphate.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Analysis of CPP-ACP, Tricalcium Phosphate, and Hydroxyapatite on Assessment of Dentinal Tubule Occlusion on Primary Enamel Using SEM: An In Vitro Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2019 Sep-Oct;12(5):371-374. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1680. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2019. PMID: 32440039 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro evaluation of remineralizing agents on dentinal tubule occlusion: A scanning electron microscopic study.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2023 Jul-Aug;27(4):362-367. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_413_22. Epub 2023 Jul 1. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2023. PMID: 37593561 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro remineralization of enamel subsurface lesions and assessment of dentine tubule occlusion from NaF dentifrices with and without calcium.J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2013 Jan-Mar;31(1):29-35. doi: 10.4103/0970-4388.112403. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2013. PMID: 23727740 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Management of Hypersensitive Dentin Using Propolis-based Herbal Desensitizing Agents: An In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopic Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021 Sep 1;22(9):1030-1034. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021. PMID: 35000948
-
Hydroxyapatite, a potent agent to reduce dentin hypersensitivity.J Pak Med Assoc. 2021 Nov;71(11):2604-2610. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.01175. J Pak Med Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34783744
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Different Fluoride Therapies on Hypersensitive Carious Lesions in Primary Teeth.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Nov 20;59(11):2042. doi: 10.3390/medicina59112042. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38004091 Free PMC article.
-
Twelve-Month Follow-Up of Different Dentinal Hypersensitivity Treatments by Photobiomodulation Therapy, Nd:YAG and Nd:YAP Lasers.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;12(12):1996. doi: 10.3390/life12121996. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556361 Free PMC article.
-
The Retention Effect of Resin-Based Desensitizing Agents on Hypersensitivity-A Randomized Controlled Trial.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;15(15):5172. doi: 10.3390/ma15155172. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35897604 Free PMC article.
-
Oyster shell-derived nano-hydroxyapatite and proanthocyanidin pretreatment on dentinal tubule occlusion and permeability before and after acid challenge-an in vitro study.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2023 Apr 10;34(4):17. doi: 10.1007/s10856-023-06724-4. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2023. PMID: 37036573 Free PMC article.
-
An Eggshell-Based Toothpaste as a Cost-Effective Treatment of Dentin Hypersensitivity.Eur J Dent. 2021 Oct;15(4):733-740. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1729676. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Eur J Dent. 2021. PMID: 34428838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parolia A, Kundabala M, Mohan M. Management of dentinal hypersensitivity: A review. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2011;39:167–79. - PubMed
-
- Addy M, Hunter ML. Can tooth brushing damage your health? Effects on oral and dental tissues. Int Dent J. 2003;53:177–86. - PubMed
-
- Cunha-Cruz J, Wataha JC, Heaton LJ, Rothen M, Sobieraj M, Scott J, et al. Northwest Practice-based Research Collaborative in Evidence-based dentistry. The prevalence of dentin hypersensitivity in general dental practices in the northwest United States. J Am Dent Assoc. 2013;144:288–96. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Taji S, Seow WK. A literature review of dental erosion in children. Aust Dent J. 2010;55:358–67. - PubMed