Hempseed Lignanamides Rich-Fraction: Chemical Investigation and Cytotoxicity towards U-87 Glioblastoma Cells
- PMID: 32110947
- PMCID: PMC7179246
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25051049
Hempseed Lignanamides Rich-Fraction: Chemical Investigation and Cytotoxicity towards U-87 Glioblastoma Cells
Abstract
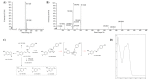
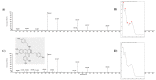
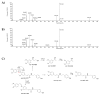
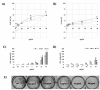
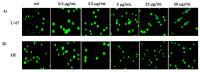
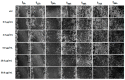
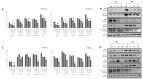
The weak but noteworthy presence of (poly)phenols in hemp seeds has been long overshadowed by the essential polyunsaturated fatty acids and digestible proteins, considered responsible for their high nutritional benefits. Instead, lignanamides and their biosynthetic precursors, phenylamides, seem to display interesting and diverse biological activities only partially clarified in the last decades. Herein, negative mode HR-MS/MS techniques were applied to the chemical investigation of a (poly)phenol-rich fraction, obtained from hemp seeds after extraction/fractionation steps. This extract contained phenylpropanoid amides and their random oxidative coupling derivatives, lignanamides, which were the most abundant compounds and showed a high chemical diversity, deeply unraveled through high resolution tandem mass spectrometry (HR-MS/MS) tools. The effect of different doses of the lignanamides-rich extract (LnHS) on U-87 glioblastoma cell line and non-tumorigenic human fibroblasts was evaluated. Thus, cell proliferation, genomic DNA damage, colony forming and wound repair capabilities were assessed, as well as LnHS outcome on the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. LnHS significantly inhibited U-87 cancer cell proliferation, but not that of fibroblasts, and was able to reduce U-87 cell migration, inducing further DNA damage. No modification in cytokines' expression level was found. Data acquired suggested that LnHS acted in U-87 cells by inducing the apoptosis machinery and suppressing the autophagic cell death.
Keywords: Cannabis sativa L.; U-87 glioblastoma cells; cytotoxicity; hemp seeds; high resolution tandem mass spectrometry; lignanamides; phenylamides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Piccolella S., Pacifico S. Plant-Derived Polyphenols: A Chemopreventive and Chemoprotectant Worth-Exploring Resource in Toxicology. In: Fishbein J.C., Heilman J.M., editors. Advances in Molecular Toxicology. Volume 9. Elsevier; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2015. pp. 161–241.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

