Differential Distribution of the wlaN and cgtB Genes, Associated with Guillain-Barré Syndrome, in Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Humans, Broiler Chickens, and Wild Birds
- PMID: 32110976
- PMCID: PMC7142995
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8030325
Differential Distribution of the wlaN and cgtB Genes, Associated with Guillain-Barré Syndrome, in Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Humans, Broiler Chickens, and Wild Birds
Abstract
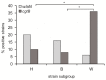
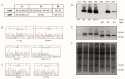
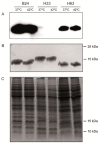
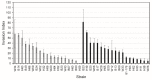
Campylobacter jejuni causes campylobacteriosis, a bacterial gastroenteritis with high incidence worldwide. Moreover, C. jejuni infection can trigger the polyneuropathic disorder denominated Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). The C. jejuni strains that can elicit GBS carry either wlaN or cgtB, coding both genes for a β-1,3-galactosyltransferase enzyme that is required for the production of sialylated lipooligosaccharide (LOSSIAL). We described a differential prevalence of the genes wlaN and cgtB in C. jejuni isolates from three different ecological niches: humans, broiler chickens, and wild birds. The distribution of both genes, which is similar between broiler chicken and human isolates and distinct when compared to the wild bird isolates, suggests a host-dependent distribution. Moreover, the prevalence of the wlaN and cgtB genes seems to be restricted to some clonal complexes. Gene sequencing identified the presence of new variants of the G- homopolymeric tract within the wlaN gene. Furthermore, we detected two variants of a G rich region within the cgtB gene, suggesting that, similarly to wlaN, the G-tract in the cgtB gene mediates the phase variation control of cgtB expression. Caco-2 cell invasion assays indicate that there is no evident correlation between the production of LOSSIAL and the ability to invade eukaryotic cells.
Keywords: Campylobacter; Guillain-Barré syndrome; cgtB; lipooligosaccharide; wlaN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Blaser M.J., Engberg J. Clinical and Epidemiological Aspects of Campylobacter Infections. In: Nachamkin I., Szymanski C., editors. Campylobacter. 3rd ed. ASM Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2008. pp. 99–121.

