Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Using Bacillus cereus SZT1 Ameliorated the Damage of Bacterial Leaf Blight Pathogen in Rice
- PMID: 32110981
- PMCID: PMC7157244
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9030160
Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Using Bacillus cereus SZT1 Ameliorated the Damage of Bacterial Leaf Blight Pathogen in Rice
Abstract
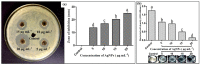
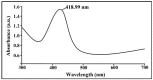
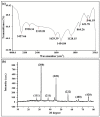
Amongst serious biotic factors deteriorating crop yield, the most destructive pathogen of rice is Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), which causes bacterial leaf blight (BLB) disease. This study involved targeted use of biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) to control BLB in order to cope with the disadvantages of chemical disease control. AgNPs were biologically synthesized from natively isolated Bacillus cereus strain SZT1, which was identified through 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Synthesis of AgNPs in bacterial culture supernatant was confirmed through UV-VIS spectroscopy. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) confirmed that the existence of AgNPs was stabilized with proteins and alcoholic groups. X-ray diffraction (XRD) data revealed the crystalline nature and imaging with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), showing the spherical shape of AgNPs with particle sizes ranging from 18 to 39 nm. The silver presence in AgNPs was further confirmed by energy dispersive spectra. Biogenic AgNPs showed substantial antibacterial activity (24.21 ± 1.01 mm) for Xoo. In a pot experiment, AgNPs were found to be effective weapons for BLB by significantly increasing the plant biomass with a decreased cellular concentration of reactive oxygen species and increased concentration of antioxidant enzyme activity.
Keywords: B. cereus; BLB; antimicrobial activity; nanotechnology; rice; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with this work.
Figures

References
-
- Zahra S.M., Wahid A., Maqbool N., Ibrahim M.H. Effect of Thiourea on Physiological Performance of Two Salt Affected Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2018;27:1–10. doi: 10.9734/ARRB/2018/41352. - DOI
-
- Li X., Xie K., Yue B., Gong Y.Y., Shao Y., Shang X., Wu Y. Inorganic arsenic contamination of rice from Chinese major rice-producing areas and exposure assessment in Chinese population. Sci. China Ser. B Chem. 2015;58:1898–1905. doi: 10.1007/s11426-015-5443-5. - DOI
-
- Khoa N.Đ., Xạ T.V., Hao L.T. Disease-reducing effects of aqueous leaf extract of Kalanchoe pinnata on rice bacterial leaf blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae involve induced resistance. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017;100:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2017.06.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
- PhosAgro/UNESCO/IUPAC/GCUF grant 82/United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
- 31872017, 31571971, 31371904, 31801787/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2017C02002; 2019C02006/Zhejiang Provincial Project
- 2017YFD0201104/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

