ZnO Nanoparticles Induced Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Mitochondrial Dysfunction and p70S6K Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 32111101
- PMCID: PMC7084801
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21051612
ZnO Nanoparticles Induced Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Mitochondrial Dysfunction and p70S6K Signaling Pathway
Abstract
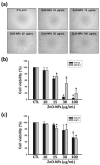
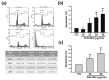
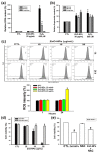
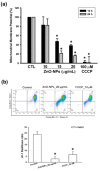
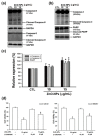
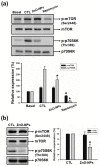
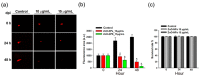
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are increasingly used in sunscreens, food additives, pigments, rubber manufacture, and electronic materials. Several studies have shown that ZnO-NPs inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis by the production of oxidative stress in a variety of human cancer cells. However, the anti-cancer property and molecular mechanism of ZnO-NPs in human gingival squamous cell carcinoma (GSCC) are not fully understood. In this study, we found that ZnO-NPs induced growth inhibition of GSCC (Ca9-22 and OECM-1 cells), but no damage in human normal keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) and gingival fibroblasts (HGF-1 cells). ZnO-NPs caused apoptotic cell death of GSCC in a concentration-dependent manner by the quantitative assessment of oligonucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Flow cytometric analysis of cell cycle progression revealed that sub-G1 phase accumulation was dramatically induced by ZnO-NPs. In addition, ZnO-NPs increased the intracellular reactive oxygen species and specifically superoxide levels, and also decreased the mitochondrial membrane potential. ZnO-NPs further activated apoptotic cell death via the caspase cascades. Importantly, anti-oxidant and caspase inhibitor clearly prevented ZnO-NP-induced cell death, indicating the fact that superoxide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with the ZnO-NP-mediated caspase-dependent apoptosis in human GSCC. Moreover, ZnO-NPs significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (p70S6K kinase). In a corollary in vivo study, our results demonstrated that ZnO-NPs possessed an anti-cancer effect in a zebrafish xenograft model. Collectively, these results suggest that ZnO-NPs induce apoptosis through the mitochondrial oxidative damage and p70S6K signaling pathway in human GSCC. The present study may provide an experimental basis for ZnO-NPs to be considered as a promising novel anti‑tumor agent for the treatment of gingival cancer.
Keywords: gingival cancer; p70S6K pathway; superoxide; zinc oxide nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goud E., Malleedi S., Ramanathan A., Wong G.R., Hwei Ern B.T., Yean G.Y., Ann H.H., Syan T.Y., Zain R.M. Association of Interleukin-10 Genotypes and Oral Cancer Susceptibility in Selected Malaysian Population: A Case- Control Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019;20:935–941. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.3.935. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

