Comparison of frequency-domain and continuous-wave near-infrared spectroscopy devices during the immediate transition
- PMID: 32111176
- PMCID: PMC7047398
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-020-1987-4
Comparison of frequency-domain and continuous-wave near-infrared spectroscopy devices during the immediate transition
Abstract
Background: Non-invasive monitoring of cerebral tissue oxygen saturation (rcSO2) during transition is of growing interest. Different near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) techniques have been developed to measure rcSO2. We compared rcSO2 values during the immediate transition in preterm neonates measured with frequency-domain NIRS (FD-NIRS) with those measured with continuous-wave NIRS (CW-NIRS) devices in prospective observational studies.
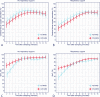
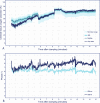
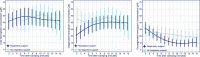
Methods: We compared rcSO2 values measured with an FD-NIRS device during the first 15 min after birth in neonates with a gestational age ≥ 30 weeks but < 37 weeks born at the Erasmus MC- Sophia Children's Hospital, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, with similar values measured with a CW-NIRS device in neonates born at the Medical University of Graz, Austria. Mixed models were used to adjust for repeated rcSO2 measurements, with fixed effects for time (non-linear), device, respiratory support and the interaction of device and respiratory support with time. Additionally, parameters such as total haemoglobin concentration and oxygenated and deoxygenated haemoglobin concentrations measured by FD-NIRS were analysed.
Results: Thirty-eight FD-NIRS measurements were compared with 58 CW-NIRS measurements. The FD-NIRS rcSO2 values were consistently higher than the CW-NIRS rcSO2 values in the first 12 min, irrespective of respiratory support. After adjustment for respiratory support, the time-dependent trend in rcSO2 differed significantly between techniques (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: As cerebral saturation measured with the FD-NIRS device differed significantly from that measured with the CW-NIRS device, differences in absolute values need to be interpreted with care. Although FD-NIRS devices have technical advantages over CW-NIRS devices, FD-NIRS devices may overestimate true cerebral oxygenation and their benefits might not outweigh the usability of the more clinically viable CW-NIRS devices.
Keywords: Continuous-wave; Frequency-domain; Near-infrared spectroscopy; Preterm neonate; Transition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Frequency-domain vs continuous-wave near-infrared spectroscopy devices: a comparison of clinically viable monitors in controlled hypoxia.J Clin Monit Comput. 2017 Oct;31(5):967-974. doi: 10.1007/s10877-016-9942-5. Epub 2016 Oct 24. J Clin Monit Comput. 2017. PMID: 27778208 Free PMC article.
-
The validity and reliability of continuous-wave near-infrared spectroscopy for the assessment of leg blood volume during an orthostatic challenge.Atherosclerosis. 2016 Aug;251:234-239. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.06.030. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Atherosclerosis. 2016. PMID: 27415611
-
Reference Ranges for Cerebral Tissue Oxygen Saturation Index in Term Neonates during Immediate Neonatal Transition after Birth.Neonatology. 2015;108(4):283-6. doi: 10.1159/000438450. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Neonatology. 2015. PMID: 26330229
-
Early Skin-to-Skin Contact Does Not Affect Cerebral Tissue Oxygenation in Preterm Infants <32 Weeks of Gestation.Children (Basel). 2022 Feb 6;9(2):211. doi: 10.3390/children9020211. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of recent advances in frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy technologies [Invited].Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Jun 12;14(7):3234-3258. doi: 10.1364/BOE.484044. eCollection 2023 Jul 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 37497520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maximizing the Reliability and Precision of Measures of Prefrontal Cortical Oxygenation Using Frequency-Domain Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;24(8):2630. doi: 10.3390/s24082630. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38676247 Free PMC article.
-
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI).Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 24;21(5):1586. doi: 10.3390/s21051586. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gas in scattering media absorption spectroscopy as a potential tool in neonatal respiratory care.Pediatr Res. 2022 Nov;92(5):1240-1246. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02110-y. Epub 2022 May 23. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 35606473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pansy J, Baik N, Schwaberger B, Scheuchenegger A, Pichler-Stachl E, Avian A, et al. Cerebral hypoxia during immediate transition after birth and short term neurological outcome. Early Hum Dev. 2017;110:13–15. - PubMed
-
- Verhagen EA, Van Braeckel KN, van der Veere CN, Groen H, Dijk PH, Hulzebos CV, et al. Cerebral oxygenation is associated with neurodevelopmental outcome of preterm children at age 2 to 3 years. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2015;57(5):449–455. - PubMed
-
- Schneider A, Minnich B, Hofstatter E, Weisser C, Hattinger-Jurgenssen E, Wald M. Comparison of four near-infrared spectroscopy devices shows that they are only suitable for monitoring cerebral oxygenation trends in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2014;103(9):934–938. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

