The burden of unrecognised chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes at a county hospital clinic in Kenya: implications to care and need for screening
- PMID: 32111192
- PMCID: PMC7048110
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-020-1705-3
The burden of unrecognised chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes at a county hospital clinic in Kenya: implications to care and need for screening
Abstract
Background: Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in patients with type 2 diabetes enhances the cardiovascular risk profiles and disease, and is a strong predictor of progression to end-stage kidney disease. Early diagnosis is encouraged for referral to specialist kidney care to initiate active management that would optimize outcomes including forestalling progression to end-stage kidney disease. This study was conducted in a regional referral public health facility in Central Kenya with a high prevalence of type 2 diabetes. It was aimed at finding out the burden of undiagnosed chronic kidney disease in their clinic of ambulatory patients with type 2 diabetes who dwell mainly in the rural area.
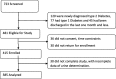
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted at the out-patient of Nyeri County hospital. A total of 385 patients were enrolled over 5 months. Informed consent was obtained and clinical evaluation was done, a spot sample of urine obtained for albuminuria and venous blood drawn for HbA1c, Lipids and serum creatinine. Estimated GFR (eGFR) was calculated using the Cockroft-Gault equation. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) was classified on KDIGO scale. Albuminuria was reported as either positive or negative. Descriptive statistics for data summary and regression analysis were employed on SPSS v23.
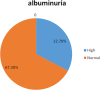
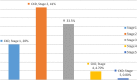
Results: A total of 385 participants were included in the study, 252 (65.5%) were females. There were 39.0% (95%CI 34.3-44.2) patients in CKD/KDIGO stages 3, 4 and 5 and 32.7% (95%CI, 27.8-37.4) had Albuminuria. The risk factors that were significantly associated with chronic kidney disease/KDIGO stages 3, 4 and 5 were: age > 50 years, long duration with diabetes > 5 years and hypertension. Employment and paradoxically, obesity reduced the odds of having CKD, probably as markers of better socio-economic status.
Conclusion: Unrecognized CKD of KDIGO stages 3,4 and 5 occurred in over 30 % of the study patients. The risk factors of hypertension, age above 50, long duration of diabetes should help identify those at high risk of developing CKD, for screening and linkage to care. They are at high risk of progression to end-stage kidney disease and cardiovascular events. The imperative of screening for chronic kidney disease is availing care in publicly-funded hospitals.
Conflict of interest statement
There are none served by this research and publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adequacy of control of cardiovascular risk factors in ambulatory patients with type 2 diabetes attending diabetes out-patients clinic at a county hospital, Kenya.BMC Endocr Disord. 2017 Dec 1;17(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12902-017-0223-1. BMC Endocr Disord. 2017. PMID: 29191193 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High prevalence of chronic kidney disease in Finnish patients with type 2 diabetes treated in primary care.Prim Care Diabetes. 2015 Feb;9(1):31-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2014.06.001. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Prim Care Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25066820
-
Prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease and diabetic kidney disease in a central Chinese urban population: a cross-sectional survey.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Apr 3;21(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01761-5. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32245423 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Early Diagnosis and Monitoring of Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Addressing the Barriers to Albuminuria Testing.J Prim Care Community Health. 2021 Jan-Dec;12:21501327211003683. doi: 10.1177/21501327211003683. J Prim Care Community Health. 2021. PMID: 33749371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Making an impact on kidney disease in people with type 2 diabetes: the importance of screening for albuminuria.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022 Jul;10(4):e002806. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2022-002806. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022. PMID: 35790319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of nephropathy among patients with diabetes mellitus in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2025 Apr 25;6:1551088. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2025.1551088. eCollection 2025. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40351523 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and associated factors of overweight and obesity among persons with type 2 diabetes in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):696-713. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2182909. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 36821504 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription pattern, glycemic control status, and predictors of poor glycemic control among diabetic patients with comorbid chronic kidney disease in Ethiopia: a facility-based cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Feb 3;25(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01853-z. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 39901138 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of dyslipidemia among persons with type 2 diabetes in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 May 6;86(6):3468-3477. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002122. eCollection 2024 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38846843 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated factors among adult diabetic patients: a hospital-based cross-sectional study.Front Epidemiol. 2024 Nov 19;4:1467911. doi: 10.3389/fepid.2024.1467911. eCollection 2024. Front Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 39628978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ninomiya T, Perkovic V, de Galan BE, Zoungas S, Pillai A, Jardine M, Patel A, Cass A, Neal B, Poulter N, Mogensen CE, Cooper M, Marre M, Williams B, Hamet P, Mancia G, Woodward M, Macmahon S, Chalmers J, ADVANCE Collaborative Group Albuminuria and kidney function independently predict cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(8):1813–1821. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008121270. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sasso FC, Chiodini P, Carbonara O, De Nicola L, Conte G, Salvatore T, Nasti R, Marfella R, Gallo C, Signoriello S, Torella R, Minutolo R. High cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy: the predictive role of albuminuria and glomerular filtration rate. The NID-2 prospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27:2269–2274. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr644. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

