Potential Protective Effects of the Water-Soluble Chinese Propolis on Hypertension Induced by High-Salt Intake
- PMID: 32112504
- PMCID: PMC7938408
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.12770
Potential Protective Effects of the Water-Soluble Chinese Propolis on Hypertension Induced by High-Salt Intake
Abstract
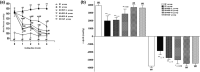
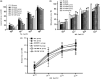
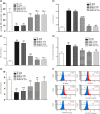
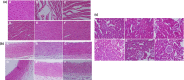
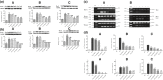
High-salt (HS) intake is closely associated with the ignition and progression of hypertension. The mechanisms might be involved in endothelial dysfunction, nitric oxide deficiency, oxidative stress, and proinflammatory cytokines. Propolis is widely used as a natural antioxidant and is a well-known functional food for its biological activities, which includes anti-inflammation, antimicrobial, and liver detoxification. In this study, we successfully replicated a HS diet-induced hypertensive rat model. We found that in the long-term HS diet group, the myocardial function of the rats was altered and led to a significant decrease (around 49%) in heart function. However, doses of Chinese water-soluble propolis (WSP) were found directly proportional (11%, 60%, 91%, respectively) to the myocardial function improvement in hypertensive rats. The results from the blood circulation test and hematoxylin-eosin stains showed that propolis had protective effects on myocardial functions and blood vessels in hypertensive rats. Also, based on the results of western blot and polymerase chain reaction, WSP effectively regulated Nox2 and Nox4 levels and was responsible for a decrease in reactive oxygen species synthesis. Our findings demonstrate that Chinese WSP has a significant effect on the blood pressure of hypertensive rats and their cardiovascular functions that improved significantly. The improvement in the cardiovascular functions might be related to the process of anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation, and the improvements of the endothelial function in hypertensive rats.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Kendig, M.D. & Morris, M.J. Reviewing the effects of dietary salt on cognition: mechanisms and future directions. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 28, 6–14 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Takashima, M. , Ichihara, K. & Hirata, Y. Neuroprotective effects of Brazilian green propolis on oxytosis/ferroptosis in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 132, 110669 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

