Cxcr6-Based Mesenchymal Stem Cell Gene Therapy Potentiates Skin Regeneration in Murine Diabetic Wounds
- PMID: 32112713
- PMCID: PMC7210709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.02.014
Cxcr6-Based Mesenchymal Stem Cell Gene Therapy Potentiates Skin Regeneration in Murine Diabetic Wounds
Abstract
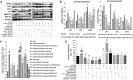
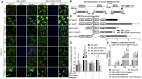
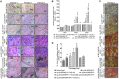
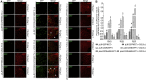
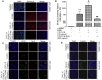
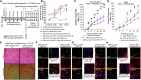
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapies for wound healing are often compromised due to low recruitment and engraftment of transplanted cells, as well as delayed differentiation into cell lineages for skin regeneration. An increased expression of chemokine ligand CXCL16 in wound bed and its cognate receptor, CXCR6, on murine bone-marrow-derived MSCs suggested a putative therapeutic relevance of exogenous MSC transplantation therapy. Induction of the CXCL16-CXCR6 axis led to activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), Src, and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2)-mediated matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 promoter regulation and expression, the migratory signaling pathways in MSC. CXCL16 induction also increased the transdifferentiation of MSCs into endothelial-like cells and keratinocytes. Intravenous transplantation of allogenic stable MSCs with Cxcr6 gene therapy potentiated skin tissue regeneration by increasing recruitment and engraftment as well as neovascularization and re-epithelialization at the wound site in excisional splinting wounds of type I and II diabetic mice. This study suggests that activation of the CXCL16-CXCR6 axis in bioengineered MSCs with Cxcr6 overexpression provides a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of diabetic wounds.
Keywords: CXCR6; cell recruitment and engraftment; cell transplantation; diabetic wound healing; full thickness excisional splinting wound model; gene therapy; mesenchymal stem cells; molecular signaling; skin regeneration; type I (Streptozotocin-induced) and type II (db/db) diabetic mice.
Copyright © 2020 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Belema-Bedada F., Uchida S., Martire A., Kostin S., Braun T. Efficient homing of multipotent adult mesenchymal stem cells depends on FROUNT-mediated clustering of CCR2. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2:566–575. - PubMed
-
- Kroeze K.L., Jurgens W.J., Doulabi B.Z., van Milligen F.J., Scheper R.J., Gibbs S. Chemokine-mediated migration of skin-derived stem cells: predominant role for CCL5/RANTES. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2009;129:1569–1581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

