FGFR1 and FGFR4 oncogenicity depends on n-cadherin and their co-expression may predict FGFR-targeted therapy efficacy
- PMID: 32114392
- PMCID: PMC7047190
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102683
FGFR1 and FGFR4 oncogenicity depends on n-cadherin and their co-expression may predict FGFR-targeted therapy efficacy
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR)1 and FGFR4 have been associated with tumorigenesis in a variety of tumour types. As a therapeutic approach, their inhibition has been attempted in different types of malignancies, including lung cancer, and was initially focused on FGFR1-amplified tumours, though with limited success.
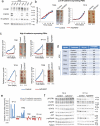
Methods: In vitro and in vivo functional assessments of the oncogenic potential of downregulated/overexpressed genes in isogenic cell lines were performed, as well as inhibitor efficacy tests in vitro and in vivo in patient-derived xenografts (PDXs). mRNA was extracted from FFPE non-small cell lung cancer samples to determine the prognostic potential of the genes under study.
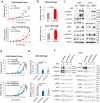
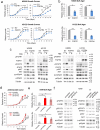
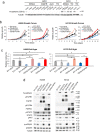
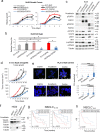
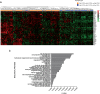
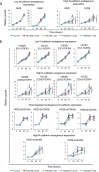
Findings: We provide in vitro and in vivo evidence showing that expression of the adhesion molecule N-cadherin is key for the oncogenic role of FGFR1/4 in non-small cell lung cancer. According to this, assessment of the expression of genes in different lung cancer patient cohorts showed that FGFR1 or FGFR4 expression alone showed no prognostic potential, and that only co-expression of FGFR1 and/or FGFR4 with N-cadherin inferred a poorer outcome. Treatment of high-FGFR1 and/or FGFR4-expressing lung cancer cell lines and patient-derived xenografts with selective FGFR inhibitors showed high efficacy, but only in models with high FGFR1/4 and N-cadherin expression.
Interpretation: Our data show that the determination of the expression of FGFR1 or FGFR4 alone is not sufficient to predict anti-FGFR therapy efficacy; complementary determination of N-cadherin expression may further optimise patient selection for this therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: FGFR inhibitors; FGFR1; FGFR4; N-cadherin; Predictive biomarker.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Drs Quintanal-Villalonga, Molina-Pinelo, Carnero, Paz-Ares, and Ferrer jointly hold patent WO2019012174A1 and patent WO2019016422A1 (pending). Dr. Paz-Ares also reports personal fees from Roche, Lilly, MSD, BMS, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Takeda, Novartis, Merck Serono, Amgen, Sanofi, Pharmamar, Clovis Oncology and Janssen outside the submitted work. JZ reports personal fees from Guardant Health. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Heist R.S., Engelman J.A. SnapShot: non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(3):448. e2. - PubMed
-
- Casaluce F., Sgambato A., Maione P., Rossi A., Ferrara C., Napolitano A. ALK inhibitors: a new targeted therapy in the treatment of advanced NSCLC. Target Oncol. 2013;8(1):55–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

