Salvage ipilimumab associated with a significant response in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32114501
- PMCID: PMC7057424
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000584
Salvage ipilimumab associated with a significant response in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Metastatic sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma (sRCC) is an aggressive variant of RCC with generally poor prognosis. Treatment with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors or chemotherapy generates only short-lived responses. Recent research has suggested a role for combination checkpoint inhibition as first line treatment for metastatic sRCC. This therapy consists of induction with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 inhibitor, ipilimumab, administered with programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitor, nivolumab. After completion of four cycles of combination therapy, single-agent maintenance nivolumab is recommended until progression. Patients who progress on maintenance nivolumab are switched to alternate therapy. Herein, we present a case of a patient with RCC who progressed on maintenance nivolumab who, on retreatment with ipilimumab, demonstrated a significant response In addition, we summarize important findings to support the role of salvage ipilimumab in patients with sRCC.
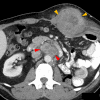
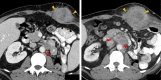
Case presentation: A 46-year-old man presented with flank pain and hematuria, the work up of which noted a left kidney mass for which he underwent nephrectomy and was diagnosed with localized sRCC with 60% sarcomatoid differentiation. Within 3 months of nephrectomy, he presented with recurrent flank pain and was diagnosed with recurrence of disease. He was treated with ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg for four doses and demonstrated a partial response. He was then transitioned to single agent nivolumab maintenance. After 3 months on maintenance therapy, he was noted to have progression of disease. Given prior response to immune check point combination, it was decided to rechallenge the patient with 1 mg/kg ipilimumab. After two doses of ipilimumab and nivolumab combination therapy, the patient was noted to have a partial response. He maintained a response for an additional 9 months and treatment was eventually discontinued due to grade 3 toxicity and progression.
Conclusions: This case report demonstrates the utility of retreatment with ipilimumab as a salvage option for patients progressing on maintenance PD-1 inhibitors in metastatic RCC. Further studies are needed to identify predictors of response and toxicity to this approach, as well as the optimal scheduling of ipilimumab with maintenance nivolumab.
Keywords: case reports.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salvage Ipilimumab and Nivolumab in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma After Prior Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Sep 20;38(27):3088-3094. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.03315. Epub 2020 Jun 3. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32491962 Free PMC article.
-
Safe and effective use of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in a patient with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid dedifferentiation and end stage renal disease on hemodialysis.Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2021;27:100349. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2021.100349. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33725559 Free PMC article.
-
PRISM protocol: a randomised phase II trial of nivolumab in combination with alternatively scheduled ipilimumab in first-line treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 14;19(1):1102. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6273-1. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31727024 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ipilimumab in combination with nivolumab for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018 Sep;18(9):947-957. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2018.1513485. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30124333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salvage nivolumab and ipilimumab after prior anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2022 Apr;11(7):1669-1677. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4587. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35138046 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Atypical Response Patterns in Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-Navigating the Radiologic Potpourri.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 2;13(7):1689. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071689. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918397 Free PMC article.
-
First-line axitinib therapy is less effective in metastatic renal cell carcinoma with spindle histology.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 18;10(1):20089. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77135-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33208816 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcomatoid urothelial carcinoma of the renal pelvis treated with immunotherapy.BMC Urol. 2023 Mar 18;23(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01210-z. BMC Urol. 2023. PMID: 36934227 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
