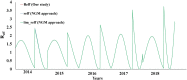
Letter to the editor in response to 'Seasonality of the transmissibility of hand, foot and mouth disease: a modelling study in Xiamen City, China'
- PMID: 32115008
- PMCID: PMC7118357
- DOI: 10.1017/S095026882000059X
Letter to the editor in response to 'Seasonality of the transmissibility of hand, foot and mouth disease: a modelling study in Xiamen City, China'
Figures
Comment in
-
Attach importance to the procedure of deriving reproduction numbers from compartmental models: Letter to the editor in response to 'Seasonality of the transmissibility of hand, foot and mouth disease: a modelling study in Xiamen City, China'.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Mar 2;148:e62. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820000588. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32115010 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Seasonality of the transmissibility of hand, foot and mouth disease: a modelling study in Xiamen City, China.Epidemiol Infect. 2019 Dec 30;147:e327. doi: 10.1017/S0950268819002139. Epidemiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 31884976 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Attach importance to the procedure of deriving reproduction numbers from compartmental models: Letter to the editor in response to 'Seasonality of the transmissibility of hand, foot and mouth disease: a modelling study in Xiamen City, China'.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Mar 2;148:e62. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820000588. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32115010 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Seasonality of the transmissibility of hand, foot and mouth disease: a modelling study in Xiamen City, China.Epidemiol Infect. 2019 Dec 30;147:e327. doi: 10.1017/S0950268819002139. Epidemiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 31884976 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the transmissibility of hand, foot, and mouth disease by a dynamic model.Public Health. 2019 Sep;174:42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2019.05.032. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31306888
-
[Summary of research in economic burden of hand, foot, and mouth disease in China].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 10;41(2):273-279. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2020.02.023. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32164141 Chinese.
-
[Prevalence and Analyses of the Changing Etiology of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in China].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015 Sep;31(5):554-9. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26738295 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Control measures during the COVID-19 outbreak reduced the transmission of hand, foot, and mouth disease.J Saf Sci Resil. 2021 Jun;2(2):63-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jnlssr.2021.06.002. Epub 2021 Jun 11. J Saf Sci Resil. 2021. PMID: 40477419 Free PMC article.
-
The epidemiological characteristics and effectiveness of countermeasures to contain coronavirus disease 2019 in Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province, China.Sci Rep. 2021 May 5;11(1):9545. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88473-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33953243 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the effectiveness of measures to control the novel coronavirus disease 2019 in Jilin Province, China.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Mar 6;21(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-05936-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33676420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cui J-A et al. (2020) Global dynamics of an epidemiological model with acute and chronic HCV infections. Applied Mathematics Letters 103, 106203.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources