Circulating let-7g-5p and miR-191-5p Are Independent Predictors of Chronic Kidney Disease in Hypertensive Patients
- PMID: 32115655
- PMCID: PMC7241936
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpaa031
Circulating let-7g-5p and miR-191-5p Are Independent Predictors of Chronic Kidney Disease in Hypertensive Patients
Abstract
Background: Hypertension (HTN) is associated with target organ damage such as cardiac, vascular, and kidney injury. Several studies have investigated circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) as biomarkers of cardiovascular disease, but few have examined them as biomarker of target organ damage in HTN. We aimed to identify circulating miRNAs that could serve as biomarkers of HTN-induced target organ damage using an unbiased approach.
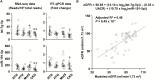
Methods and results: Fifteen normotensive subjects, 16 patients with HTN, 15 with HTN associated with other features of the metabolic syndrome (MetS), and 16 with HTN or chronic kidney disease (CKD) were studied. Circulating RNA extracted from platelet-poor plasma was used for small RNA sequencing. Differentially expressed (DE) genes were identified with a threshold of false discovery rate <0.1. DE miRNAs were identified uniquely associated with HTN, MetS, or CKD. However, only 2 downregulated DE miRNAs (let-7g-5p and miR-191-5p) could be validated by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. Let-7g-5p was associated with large vessel stiffening, miR-191-5p with MetS, and both miRNAs with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and neutrophil and lymphocyte fraction or number and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Using the whole population, stepwise multiple linear regression generated a model showing that let-7g-5p, miR-191-5p, and urinary albumin/creatinine ratio predicted eGFR with an adjusted R2 of 0.46 (P = 8.5e-7).
Conclusions: We identified decreased circulating let-7g-5p and miR-191-5p as independent biomarkers of CKD among patients with HTN, which could have pathophysiological and therapeutic implications.
Keywords: biomarker; blood pressure; hypertension; microRNA; target organ damage.
© American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd 2020. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the associations between circulating microRNAs and kidney function in coronary angiography patients.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Feb 1;318(2):F315-F321. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00429.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31813253
-
Subclinical Kidney Damage in Hypertensive Patients: A Renal Window Opened on the Cardiovascular System. Focus on Microalbuminuria.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:279-306. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_85. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27873229 Review.
-
Associations of Circulating MicroRNAs (miR-17, miR-21, and miR-150) and Chronic Kidney Disease in a Japanese Population.J Epidemiol. 2020 Apr 5;30(4):177-182. doi: 10.2188/jea.JE20180233. Epub 2019 Mar 23. J Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 30905898 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma microRNA-155-5p is increased among patients with chronic kidney disease and nocturnal hypertension.J Am Soc Hypertens. 2017 Dec;11(12):831-841.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 28. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 29146158
-
Epidemiology of hypertension in CKD.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015 Mar;22(2):88-95. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2014.09.004. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25704344 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Biomarkers for Hypertension-Mediated Organ Damage Detection: A Narrative Review.Biomedicines. 2024 May 12;12(5):1071. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051071. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring New Kingdoms: The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Oxi-Inflamm-Aging Related to Cardiorenal Syndrome.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;11(1):78. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010078. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum MicroRNA-191-5p Levels in Vascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes: The EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Dec 21;109(1):e163-e174. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad468. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37552780 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs associated with chronic kidney disease in the general population and high-risk subgroups: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2022 Feb 16;12(2):e057500. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-057500. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35173010 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Changes Up to 24 h following Induced Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 24;23(23):14696. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314696. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499023 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Frohlich ED, Apstein C, Chobanian AV, Devereux RB, Dustan HP, Dzau V, Fauad-Tarazi F, Horan MJ, Marcus M, Massie B. The heart in hypertension. N Engl J Med 1992; 327:998–1008. - PubMed
-
- Boutouyrie P, Laurent S, Girerd X, Benetos A, Lacolley P, Abergel E, Safar M. Common carotid artery stiffness and patterns of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 1995; 25:651–659. - PubMed
-
- Park JB, Schiffrin EL. Small artery remodeling is the most prevalent (earliest?) form of target organ damage in mild essential hypertension. J Hypertens 2001; 19:921–930. - PubMed
-
- Mulè G, Castiglia A, Cusumano C, Scaduto E, Geraci G, Altieri D, Di Natale E, Cacciatore O, Cerasola G, Cottone S. Subclinical kidney damage in hypertensive patients: a renal window opened on the cardiovascular system. focus on microalbuminuria. Adv Exp Med Biol 2017; 956:279–306. - PubMed
-
- Rao MV, Qiu Y, Wang C, Bakris G. Hypertension and CKD: Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) and National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1999–2004. Am J Kidney Dis 2008; 51(Suppl 2):S30–S37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

