Roles of PTBP1 in alternative splicing, glycolysis, and oncogensis
- PMID: 32115910
- PMCID: PMC7076342
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1900422
Roles of PTBP1 in alternative splicing, glycolysis, and oncogensis
Abstract
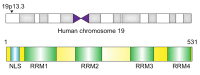
Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 (PTBP1) plays an essential role in splicing and is expressed in almost all cell types in humans, unlike the other proteins of the PTBP family. PTBP1 mediates several cellular processes in certain types of cells, including the growth and differentiation of neuronal cells and activation of immune cells. Its function is regulated by various molecules, including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and RNA-binding proteins. PTBP1 plays roles in various diseases, particularly in some cancers, including colorectal cancer, renal cell cancer, breast cancer, and glioma. In cancers, it acts mainly as a regulator of glycolysis, apoptosis, proliferation, tumorigenesis, invasion, and migration. The role of PTBP1 in cancer has become a popular research topic in recent years, and this research has contributed greatly to the formulation of a useful therapeutic strategy for cancer. In this review, we summarize recent findings related to PTBP1 and discuss how it regulates the development of cancer cells.
Keywords: Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 (PTBP1); Alternative splicing; Glycolysis; M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase (PKM2); Cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

