Laminin and Integrin in LAMA2-Related Congenital Muscular Dystrophy: From Disease to Therapeutics
- PMID: 32116540
- PMCID: PMC7026472
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00001
Laminin and Integrin in LAMA2-Related Congenital Muscular Dystrophy: From Disease to Therapeutics
Abstract
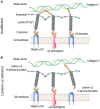
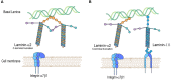
Laminin-α2-related congenital muscular dystrophy (LAMA2-CMD) is a devastating neuromuscular disease caused by mutations in the LAMA2 gene. These mutations result in the complete absence or truncated expression of the laminin-α2 chain. The α2-chain is a major component of the laminin-211 and laminin-221 isoforms, the predominant laminin isoforms in healthy adult skeletal muscle. Mutations in this chain result in progressive skeletal muscle degeneration as early as neonatally. Laminin-211/221 is a ligand for muscle cell receptors integrin-α7β1 and α-dystroglycan. LAMA2 mutations are correlated with integrin-α7β1 disruption in skeletal muscle. In this review, we will summarize laminin-211/221 interactions with integrin-α7β1 in LAMA2-CMD muscle. Additionally, we will summarize recent developments using upregulation of laminin-111 in the sarcolemma of laminin-α2-deficient muscle. We will discuss potential mechanisms of action by which laminin-111 is able to prevent myopathy. These published studies demonstrate that laminin-111 is a disease modifier of LAMA2-CMD through different methods of delivery. Together, these studies show the potential for laminin-111 therapy as a novel paradigm for the treatment of LAMA2-CMD.
Keywords: LAMA2-CMD; Laminin; muscle; muscular dystrophy; therapeutic; α7 integrin.
Copyright © 2020 Barraza-Flores, Bates, Oliveira-Santos and Burkin.
Figures
References
-
- Barraza-Flores P., Fontelonga T. M., Wuebbles R. D., Hermann H. J., Nunes A. M., Kornegay J. N., et al. (2019). Laminin-111 protein therapy enhances muscle regeneration and repair in the GRMD dog model of duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 28, 2686–2695. 10.1093/hmg/ddz086 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

