Osmoregulated Periplasmic Glucans Transmit External Signals Through Rcs Phosphorelay Pathway in Yersinia enterocolitica
- PMID: 32117145
- PMCID: PMC7013093
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00122
Osmoregulated Periplasmic Glucans Transmit External Signals Through Rcs Phosphorelay Pathway in Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
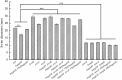
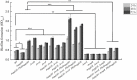
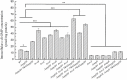
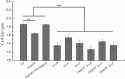
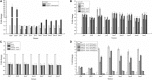
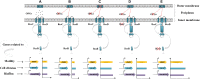
Fast response to environmental changes plays a key role in the transmission and pathogenesis of Yersinia enterocolitica. Osmoregulated periplasmic glucans (OPGs) are known to be involved in environmental perception of several Enterobacteriaceae pathogens; however, the biological function of OPGs in Y. enterocolitica is still unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of OPGs in Y. enterocolitica by deleting the opgGH operon encoding enzymes responsible for OPGs biosynthesis. Complete loss of OPGs in the ΔopgGH mutant resulted in decreased motility, c-di-GMP production, biofilm formation and smaller cell size, whereas the overproduction of OPGs through restoration of opgGH expression promoted c-di-GMP/biofilm production and increased antibiotic resistance of Y. enterocolitica. Gene expression analysis revealed that opgGH deletion reduced transcription of flhDC, ftsAZ, hmsT and hmsHFRS genes regulated by the Rcs phosphorelay system, whereas additional deletion of rcs family genes (rcsF, rcsC, or rcsB) reversed this effect and restored motility and c-di-GMP/biofilm production but further reduced cell size. Furthermore, disruption of the Rcs phosphorelay increased the motility and promoted the induction of biofilm and c-di-GMP production regulated by OPGs through upregulating the expression of flhDC, hmsHFRS, and hmsT. However, deletion of genes encoding the EnvZ/OmpR phosphorelay downregulated the flhDC, hmsHFRS and hmsT expression, leading to the decreased motility and prevented the induction of biofilm and c-di-GMP production regulated by OPGs. These results indicated that Rcs phosphorelay had the effect on OPGs-mediated functional responses in Y. enterocolitica. Our findings disclose part of the biological role of OPGs and the underlying molecular mechanisms associated with Rcs system in the regulation of the pathogenic phenotype in Y. enterocolitica.
Keywords: EnvZ/OmpR phosphorelay; Rcs phosphorelay; Yersinia enterocolitica; gene expression; osmoregulated periplasmic glucans; pathogenic phenotype.
Copyright © 2020 Meng, Huang, Huang, Liu, Han and Chen.
Figures


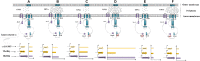
Similar articles
-
The role of osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in the biofilm antibiotic resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica.Microb Pathog. 2020 Oct;147:104284. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104284. Epub 2020 May 31. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32492459
-
Differential regulation of physiological activities by RcsB and OmpR in Yersinia enterocolitica.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019 Sep 1;366(17):fnz210. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnz210. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31598670
-
An Osmoregulatory Mechanism Operating through OmpR and LrhA Controls the Motile-Sessile Switch in the Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Pantoea alhagi.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 May 2;85(10):e00077-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00077-19. Print 2019 May 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30902852 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the biological role of the osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in pathogenic and symbiotic bacteria.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2015 Oct;7(5):690-7. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12325. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26265506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Rcs phosphorelay: more than just a two-component pathway.Future Microbiol. 2010 Aug;5(8):1173-84. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.83. Future Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20722597 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the Two-Component System PhoP/PhoQ in Intrinsic Resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica to Polymyxin.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 10;13:758571. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.758571. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35222323 Free PMC article.
-
Fur Represses Vibrio cholerae Biofilm Formation via Direct Regulation of vieSAB, cdgD, vpsU, and vpsA-K Transcription.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 22;11:587159. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.587159. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33193241 Free PMC article.
-
The implication of viability and pathogenicity by truncated lipopolysaccharide in Yersinia enterocolitica.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;107(23):7165-7180. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12785-w. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37728625
-
Similar and Divergent Roles of Stringent Regulator (p)ppGpp and DksA on Pleiotropic Phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0205522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02055-22. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36409141 Free PMC article.
-
The Rcs System Contributes to the Motility Defects of the Twin-Arginine Translocation System Mutant of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2022 Apr 19;204(4):e0061221. doi: 10.1128/jb.00612-21. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35311558 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

