Radioimmunotherapy of Blastomycosis in a Mouse Model With a (1→3)-β-Glucans Targeting Antibody
- PMID: 32117166
- PMCID: PMC7019017
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00147
Radioimmunotherapy of Blastomycosis in a Mouse Model With a (1→3)-β-Glucans Targeting Antibody
Abstract
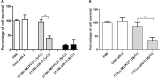
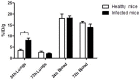
Invasive fungal infections (IFI) cause devastating morbidity and mortality, with the number of IFIs more than tripling since 1979. Our laboratories were the first to demonstrate that radiolabeled microorganism-specific monoclonal antibodies are highly effective for treatment of experimental fungal, bacterial and viral infections. Later we proposed to utilize surface expressed pan-antigens shared by major IFI-causing pathogens such as beta-glucans as RIT targets. Here we evaluated in vivo RIT targeting beta-glucan in Blastomyces dermatitidis which causes serious infections in immunocompromised and immunocompetent individuals and in companion dogs. B. dermatitidis cells were treated with the 400-2 antibody to (1→3)-β-glucans radiolabeled with the beta-emitter 177Lutetium (177Lu) and alpha-emitter 213Bismuth (213Bi) and the efficacy of cell kill was determined by colony forming units (CFUs). To determine the antigen-specific localization of the 400-2 antibody in vivo, C57BL6 mice were infected intratracheally with 2 × 105 B. dermatitidis cells and given 111In-400-2 antibody 24 h later. To evaluate the killing of B. dermatitidis cells with RIT, intratracheally infected mice were treated with 150 μCi 213Bi-400-2 and their lungs analyzed for CFUs 96 h post-infection. 213Bi-400-2 proved to be more effective in killing B. dermatitidis cells in vitro than 177Lu-400-2. Three times more 111In-400-2 accumulated in the lungs of infected mice, than in the non-infected ones. 213Bi-400-2 lowered the fungal burden in the lungs of infected mice more than 2 logs in comparison with non-treated infected controls. In conclusion, our results demonstrate the ability of an anti-(1-3)-beta-D-glucan antibody armed with an alpha-emitter 213Bi to selectively kill B. dermatitidis cells in vitro and in vivo. These first in vivo results of the effectiveness of RIT targeting pan-antigens on fungal pathogens warrant further investigation.
Keywords: (1→3)-β-glucan; 213Bismuth; Blastomyces dermatitidis; mouse model; radioimmunotherapy.
Copyright © 2020 Helal, Allen, van Dijk, Nosanchuk, Snead and Dadachova.
Figures


References
-
- Bryan R. A., Huang X., Morgenstern A., Bruchertseifer F., Casadevall A., Dadachova E. (2008). Radiofungicidal effects of external gamma radiation and antibody-targeted beta and alpha radiation on Cryptococcus neoformans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 2232–2235. 10.1128/AAC.01245-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

