HTLV-1 Infection and Rheumatic Diseases
- PMID: 32117170
- PMCID: PMC7025999
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00152
HTLV-1 Infection and Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
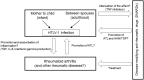
Some major research and clinical questions about human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection and rheumatic diseases remain: (1) Does HTLV-1 infection cause rheumatic diseases? (2) Do patients with rheumatic diseases display different responses to treatment with anti-rheumatic agents when they are HTLV-1 carriers? (3) Is adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) or HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) more prevalent in HTLV-1 carriers with rheumatic diseases who are treated with anti-rheumatic agents? These questions are important because increasing numbers of patients with rheumatic diseases are currently receiving treatment with aggressive medicines such as immunosuppressants and biologics. Studies on HTLV-1 gene-transgenic mice have shown manifestations resembling rheumatic diseases. Epidemiological studies have shown a high incidence of HTLV-1 infection in patients with rheumatic diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Sjogren's syndrome, and polymyositis. HTLV-1-positive and HTLV-1-negative patients with RA have displayed similar immunological features including the seroprevalence of anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies. Conversely, attenuated effectiveness of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for HTLV-1-positive patients with RA in Japan has been reported. Therefore, although no direct evidence has shown that HTLV-1 infection alone causes rheumatic diseases, HTLV-1 may affect the inflammation of RA. Although the incidence of ATL or HAM/TSP among patients with rheumatic diseases has not been investigated in large-scale studies, ATL or HAM/TSP has developed among HTLV-1-positive patients with rheumatic diseases. HTLV-1 infection may affect the clinical course of patients with rheumatic diseases, particularly after receiving anti-rheumatic agents. Because studies on these issues are limited, further investigation with large sample sizes is necessary.
Keywords: HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis; adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma; disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; human T-cell leukemia virus type 1; rheumatic diseases; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2020 Umekita and Okayama.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous