Antibacterial Peptide BSN-37 Kills Extra- and Intra-Cellular Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium by a Nonlytic Mode of Action
- PMID: 32117178
- PMCID: PMC7019029
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00174
Antibacterial Peptide BSN-37 Kills Extra- and Intra-Cellular Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium by a Nonlytic Mode of Action
Abstract
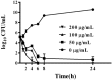
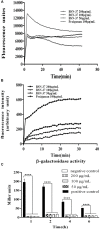
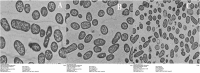
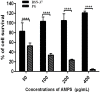
The increasing rates of resistance to traditional anti-Salmonella agents have made the treatment of invasive salmonellosis more problematic, which necessitates the search for new antimicrobial compounds. In this study, the action mode of BSN-37, a novel antibacterial peptide (AMP) from bovine spleen neutrophils, was investigated against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium). Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) and time-kill kinetics of BSN-37 were determined. The cell membrane changes of S. Typhimurium CVCC541 (ST) treated with BSN-37 were investigated by testing the fluorescence intensity of membrane probes and the release of cytoplasmic β-galactosidase activity. Likewise, cell morphological and ultrastructural changes were also observed using scanning and transmission electron microscopes. Furthermore, the cytotoxicity of BSN-37 was detected by a CCK-8 kit and real-time cell assay. The proliferation inhibition of BSN-37 against intracellular S. Typhimurium was performed in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells. The results demonstrated that BSN-37 exhibited strong antibacterial activity against ST (MICs, 16.67 μg/ml), which was not remarkably affected by the serum salts at a physiological concentration. However, the presence of CaCl2 led to an increase in MIC of BSN-37 by about 4-fold compared to that of ST. BSN-37 at the concentration of 100 μg/ml could completely kill ST after co-incubation for 6 h. Likewise, BSN-37 at different concentrations (50, 100, and 200 μg/ml) could increase the outer membrane permeability of ST but not impair its inner membrane integrity. Moreover, no broken and ruptured cells were found in the figures of scanning and transmission electron microscopes. These results demonstrate that BSN-37 exerts its antibacterial activity against S. Typhimurium by a non-lytic mode of action. Importantly, BSN-37 had no toxicity to the tested eukaryotic cells, even at a concentration of 800 μg/ml. BSN-37 could significantly inhibit the proliferation of intracellular S. Typhimurium.
Keywords: Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium; action mode; antibacterial activity; antibacterial peptide BSN-37; cytotoxicity; eukaryotic cells.
Copyright © 2020 Yang, Sun, Xu, Hang, Wang, Zhen, Hu, Chen, Xia and Hu.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial Peptide JH-3 Effectively Kills Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Strain CVCC541 and Reduces Its Pathogenicity in Mice.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019 Dec;11(4):1379-1390. doi: 10.1007/s12602-019-09533-w. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019. PMID: 31001786
-
Antibacterial Activity of Olive Oil Polyphenol Extract Against Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus: Possible Mechanisms.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2020 Jun;17(6):396-403. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2019.2713. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2020. PMID: 31755743
-
Insight into the inhibitory activity and mechanism of bovine cathelicidin BMAP 27 against Salmonella Typhimurium.Microb Pathog. 2024 Feb;187:106540. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106540. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38190945
-
Anti-Salmonella Activity of a Novel Peptide, KGGDLGLFEPTL, Derived from Egg Yolk Hydrolysate.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Dec 24;13(1):19. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13010019. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38247578 Free PMC article.
-
A Thermostable, Modified Cathelicidin-Derived Peptide With Enhanced Membrane-Active Activity Against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 13;11:592220. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.592220. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33519729 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of phage pSal-4 on chicken intestinal epithelial cells injured by Salmonella enteritidis.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Dec 4;24(1):515. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03641-6. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39627695 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Expression of Antimicrobial Peptide BSN-37 from Escherichia coli by SUMO Fusion Technology.Protein J. 2023 Oct;42(5):563-574. doi: 10.1007/s10930-023-10144-2. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Protein J. 2023. PMID: 37561256
-
Integrated lncRNA and mRNA analysis reveals the immune modulatory mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide BSN-37 in mouse peritoneal macrophages.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 2;15(1):19252. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03969-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40457006 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Cecropin A (1-7) Analogs with DNA Analyzed by Multi-spectroscopic Methods.Protein J. 2024 Apr;43(2):274-282. doi: 10.1007/s10930-023-10177-7. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Protein J. 2024. PMID: 38265732
-
Characteristics of antimicrobial peptide OaBac5mini and its bactericidal mechanism against Escherichia coli.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Feb 23;10:1123054. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1123054. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36908510 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

