Genomic recombination between infectious laryngotracheitis vaccine strains occurs under a broad range of infection conditions in vitro and in ovo
- PMID: 32119681
- PMCID: PMC7051062
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229082
Genomic recombination between infectious laryngotracheitis vaccine strains occurs under a broad range of infection conditions in vitro and in ovo
Abstract
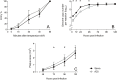
Gallid alphaherpesvirus 1 causes infectious laryngotracheitis (ILT) in farmed poultry worldwide. Intertypic recombination between vaccine strains of this virus has generated novel and virulent isolates in field conditions. In this study, in vitro and in ovo systems were co-infected and superinfected under different conditions with two genomically distinct and commonly used ILTV vaccines. The progeny virus populations were examined for the frequency and pattern of recombination events using multi-locus high-resolution melting curve analysis of polymerase chain reaction products. A varied level of recombination (0 to 58.9%) was detected, depending on the infection system (in ovo or in vitro), viral load, the composition of the inoculum mixture, and the timing and order of infection. Full genome analysis of selected recombinants with different in vitro phenotypes identified alterations in coding and non-coding regions. The ability of ILTV vaccines to maintain their capacity to recombine under such varied conditions highlights the significance of recombination in the evolution of this virus and demonstrates the capacity of ILTV vaccines to play a role in the emergence of recombinant viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Genotyping Analysis Shows That Vaccination Can Limit the Number and Diversity of Recombinant Progeny of Infectious Laryngotracheitis Viruses from the United States.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Nov 15;84(23):e01822-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01822-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30242009 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity of Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus during In Vivo Coinfection Parallels Viral Replication and Arises from Recombination Hot Spots within the Genome.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Nov 16;83(23):e01532-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01532-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28939604 Free PMC article.
-
Development and application of high-resolution melting analysis for the classification of infectious laryngotracheitis virus strains and detection of recombinant progeny.Arch Virol. 2019 Feb;164(2):427-438. doi: 10.1007/s00705-018-4086-1. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Arch Virol. 2019. PMID: 30421085 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses to infectious laryngotracheitis virus.Dev Comp Immunol. 2013 Nov;41(3):454-62. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.03.022. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23567343 Review.
-
The route of inoculation dictates the replication patterns of the infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) pathogenic strain and chicken embryo origin (CEO) vaccine.Avian Pathol. 2017 Dec;46(6):585-593. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2017.1331029. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Avian Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28532159 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Variation in the Glycoprotein B Sequence of Equid Herpesvirus 5 among Horses of Various Breeds at Polish National Studs.Pathogens. 2021 Mar 9;10(3):322. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10030322. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33803246 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Whole-Genome Sequences of Infectious laryngotracheitis Virus Isolates from Poultry Flocks in Canada: Evidence of Recombination.Viruses. 2020 Nov 12;12(11):1302. doi: 10.3390/v12111302. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33198373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- García M, Spatz S, Guy JS. Infectious laryngotracheitis 13th ed In: Swayne D, Glisson J, McDougald L, Nolan L, Suarez D, editors. Diseases of poultry. Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell; 2013. p. 161–179.
-
- Fulton RM, Schrader DL, Will M. Effect of route of vaccination on the prevention of infectious laryngotracheitis in commercial egg-laying chickens. Avian Dis. 2000;44(1):8–16. - PubMed
-
- Schneiders GH, Riblet SM, García M. Attenuation and protection efficacy of a recombinant infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) depleted of open reading frame C (Δ ORFC) when delivered in ovo. Avian diseases. 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

