Efficient immortalization of human dental pulp stem cells with expression of cell cycle regulators with the intact chromosomal condition
- PMID: 32119713
- PMCID: PMC7051082
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229996
Efficient immortalization of human dental pulp stem cells with expression of cell cycle regulators with the intact chromosomal condition
Abstract
Clinical studies have recently demonstrated that autologous transplantation of mobilized dental pulp stem cells is a safe and efficacious potential therapy for pulp regeneration. However, some limitations need to be addressed, such as the high cost of the safety and quality control tests for isolated individual dental pulp cell products before transplantation. Therefore, more efficient in vitro culturing of human dental pulp stem cells might be useful for providing low cost and high reliability testing for pulp regeneration therapy. In this study, we established a novel immortalized dental pulp stem cell line by co-expressing a mutant cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4R24C), Cyclin D1, and telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT). The established cell line maintained its original diploid chromosomes and stemness characteristics and exhibited an enhanced proliferation rate. In addition, we showed the immortalized human dental pulp stem cells still keeps their osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation abilities under appropriate culture conditions even though the cell proliferation was accelerated. Taken together, our established cell lines could serve as a useful in vitro tool for pulp regeneration therapy, and can contribute to reproducibility and ease of cell handling, thereby saving time and costs associated with safety and quality control tests.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
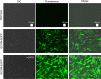



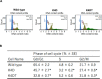



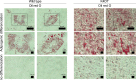
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

