Multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH and psychometric properties in gastroesophageal reflux: systematic review
- PMID: 32119822
- PMCID: PMC9432252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jped.2020.01.005
Multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH and psychometric properties in gastroesophageal reflux: systematic review
Abstract
Objective: Systematically assess studies that have analyzed the psychometric properties of multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux. Systematically verify studies that have analyzed the psychometric properties of multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH regarding the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease in pediatric patients.
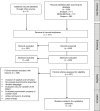
Methods: Systematic review considering specific descriptors (children and adolescents, gastroesophageal reflux disease and multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH) and their synonyms. The systematic search was carried out in the MEDLINE/Ovid, Scopus, and Embase databases, considering the period from October 2017 to December 2018. This review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), which was used for study selection. The psychometric properties described in the studies were: sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and reproducibility.
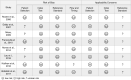
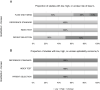
Results: Sensitivity was discussed in most studies, with a result of more than 70% in four of them. Specificity was assessed only in conjunction with sensitivity, with values from 23% to 25% in two studies, and it reached 80% in a single study. Accuracy was assessed higher than 76% in one of the selected articles. The methodological quality of the studies demonstrated low risk of bias, and there was no significant concern related to applicability of the studies.
Conclusions: According to the selected studies, multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH was considered a safe and effective tool, presenting higher sensitivity values than pHmetry regarding the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Objetivo: Avaliar sistematicamente estudos que analisaram propriedades psicométricas da impedância intraluminal multicanal associada à pHmetria (IIM-pH) no diagnóstico de refluxo gastroesofágico. Verificar sistematicamente estudos que analisaram as propriedades psicométricas de impedância intraluminal multicanal associada à pHmetria em relação ao diagnóstico da doença do refluxo gastroesofágico em pacientes pediátricos.
Métodos: Revisão sistemática que considerou descritores específicos (crianças e adolescentes, doença do refluxo gastroesofágico e impedância intraluminal multicanal associada à pHmetria) e seus sinônimos. A busca sistemática foi realizada nas bases de dados Medline/ Ovid, Scopus e Embase e considerou o período de outubro de 2017 a dezembro de 2018. Esta revisão foi realizada de acordo com o checklist Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (Prisma), usado para seleção de estudos. As propriedades psicométricas descritas nos estudos foram: sensibilidade, especificidade, acurácia e reprodutibilidade.
Resultados: A sensibilidade foi discutida na maioria dos estudos, com um resultado de mais de 70% em quatro deles. A especificidade foi avaliada apenas em conjunto com a sensibilidade, com valores em torno de 23 a 25% em dois estudos, e alcançou 80% em um único estudo. A acurácia foi avaliada em mais de 76% em um dos artigos selecionados. A qualidade metodológica dos estudos demonstrou baixo risco de viés e nenhuma consideração significativa relacionada à aplicabilidade dos estudos.
Conclusões: De acordo com os estudos selecionados, a impedância intraluminal multicanal associada à pHmetria foi considerada uma ferramenta segura e eficaz, apresentou valores de sensibilidade superiores à pHmetria no diagnóstico da doença do refluxo gastroesofágico.
Keywords: Gastroesophageal reflux; Impedance pHmetry, pediatrics; Impedância-pHmetria, pediatria; Propriedades psicométricas; Psychometric properties; Refluxo gastroesofágico.
Copyright © 2020 Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Lightdale J.R., Gremse D.A. Section on gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition. Gastroesophageal reflux: management guidance for the pediatrician. Pediatrics. 2013;131:e1684–95. - PubMed
-
- Vandenplas Y. Challenges in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants and children. Expert Opin Med Diagn. 2013;7:289–298. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira C.T., Carvalho Ed, Sdepanian V.L., Morais M.B., Vieira M.C., Silva L.R. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: exaggerations, evidence and clinical practice. J Pediatr. 2014;90:105–118. - PubMed
-
- Rosen R., Vandenplas Y., Singendonk M., Cabana M., DiLorenzo C., Gottrand F., et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;66:516–554. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical