Anti-HCV, nucleotide inhibitors, repurposing against COVID-19
- PMID: 32119961
- PMCID: PMC7089605
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117477
Anti-HCV, nucleotide inhibitors, repurposing against COVID-19
Abstract
Aims: A newly emerged Human Coronavirus (HCoV) is reported two months ago in Wuhan, China (COVID-19). Until today >2700 deaths from the 80,000 confirmed cases reported mainly in China and 40 other countries. Human to human transmission is confirmed for COVID-19 by China a month ago. Based on the World Health Organization (WHO) reports, SARS HCoV is responsible for >8000 cases with confirmed 774 deaths. Additionally, MERS HCoV is responsible for 858 deaths out of about 2500 reported cases. The current study aims to test anti-HCV drugs against COVID-19 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp).
Materials and methods: In this study, sequence analysis, modeling, and docking are used to build a model for Wuhan COVID-19 RdRp. Additionally, the newly emerged Wuhan HCoV RdRp model is targeted by anti-polymerase drugs, including the approved drugs Sofosbuvir and Ribavirin.
Key findings: The results suggest the effectiveness of Sofosbuvir, IDX-184, Ribavirin, and Remidisvir as potent drugs against the newly emerged HCoV disease.
Significance: The present study presents a perfect model for COVID-19 RdRp enabling its testing in silico against anti-polymerase drugs. Besides, the study presents some drugs that previously proved its efficiency against the newly emerged viral infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; Docking; Nucleotide inhibitors; RdRp; Sofosbuvir; Structural bioinformatics; Wuhan coronavirus.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The author declares that there is no competing interest in this work.
Figures
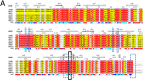

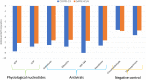
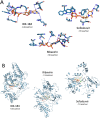
References
-
- Organization WH . World Health Organization; 2020. Surveillance Case Definitions for Human Infection With Novel Coronavirus (nCoV): Interim Guidance v1, January 2020.
-
- Organization WH . World Health Organization; 2020. Infection Prevention and Control during Health Care When Novel Coronavirus (nCoV) Infection Is Suspected: Interim Guidance, January 2020.
-
- Organization WH . World Health Organization; 2020. Laboratory Testing of Human Suspected Cases of Novel Coronavirus (nCoV) Infection: Interim Guidance, 10 January 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

