Characterization and preclinical evaluation of the cGMP grade DNA based vaccine, AV-1959D to enter the first-in-human clinical trials
- PMID: 32119976
- PMCID: PMC8772258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104823
Characterization and preclinical evaluation of the cGMP grade DNA based vaccine, AV-1959D to enter the first-in-human clinical trials
Abstract
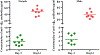
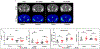
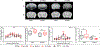
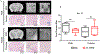
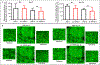
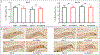
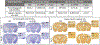
The DNA vaccine, AV-1959D, targeting N-terminal epitope of Aβ peptide, has been proven immunogenic in mice, rabbits, and non-human primates, while its therapeutic efficacy has been shown in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here we report for the first time on IND-enabling biodistribution and safety/toxicology studies of cGMP-grade AV-1959D vaccine in the Tg2576 mouse model of AD. We also tested acute neuropathology safety profiles of AV-1959D in another AD disease model, Tg-SwDI mice with established vascular and parenchymal Aβ pathology in a pre-clinical translational study. Biodistribution studies two days after the injection demonstrated high copy numbers of AV-1959D plasmid after single immunization of Tg2576 mice at the injection sites but not in the tissues of distant organs. Plasmids persisted at the injection sites of some mice 60 days after vaccination. In Tg2576 mice with established amyloid pathology, we did not observe short- or long-term toxicities after multiple immunizations with three doses of AV-1959D. Assessment of the repeated dose acute safety of AV-1959D in cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) prone Tg-SwDI mice did not reveal any immunotherapy-induced vasogenic edema detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or increased microhemorrhages. Multiple immunizations of Tg-SwDI mice with AV-1959D did not induce T and B cell infiltration, glial activation, vascular deposition of Aβ, or neuronal degeneration (necrosis and apoptosis) greater than that in the control group determined by immunohistochemistry of brain tissues. Taken together, the safety data from two different mouse models of AD substantiate a favorable safety profile of the cGMP grade AV-1959D vaccine supporting its progression to first-in-human clinical trials.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease (AD); Biodistribution; DNA Aβ-vaccine; Immunohistochemistry (IHC); Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); Mouse models of AD; Safety toxicology.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Dr. Ghochikyan and Dr. Agadjanyan are co-authors of US patent 10005825 B2. Other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
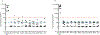
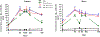
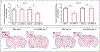
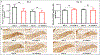

References
-
- Abdulhaqq SA, Weiner DB, 2008. DNA vaccines: developing new strategies to enhance immune responses. Immunol. Res 42, 219–232. - PubMed
-
- Agadjanyan MG, et al. , 1998. DNA plasmid based vaccination against the oncogenic human T cell leukemia virus type 1. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol 226, 175–192. - PubMed
-
- Agadjanyan MG, et al. , 2005. Prototype Alzheimer’s disease vaccine using the immunodominant B cell epitope from beta-amyloid and promiscuous T cell epitope pan HLA DR-binding peptide. J. Immunol 174, 1580–1586. - PubMed
-
- Agadjanyan M, et al. , 2009. Active and passive Aβ-immunotherapy: positive and negative outcomes from pre-clinical and clinical trials and future directions. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

