Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer
- PMID: 32121014
- PMCID: PMC7140518
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9030561
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer
Abstract
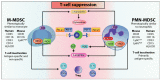
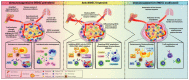
The emergence of immunotherapy has been an astounding breakthrough in cancer treatments. In particular, immune checkpoint inhibitors, targeting PD-1 and CTLA-4, have shown remarkable therapeutic outcomes. However, response rates from immunotherapy have been reported to be varied, with some having pronounced success and others with minimal to no clinical benefit. An important aspect associated with this discrepancy in patient response is the immune-suppressive effects elicited by the tumour microenvironment (TME). Immune suppression plays a pivotal role in regulating cancer progression, metastasis, and reducing immunotherapy success. Most notably, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), a heterogeneous population of immature myeloid cells, have potent mechanisms to inhibit T-cell and NK-cell activity to promote tumour growth, development of the pre-metastatic niche, and contribute to resistance to immunotherapy. Accumulating research indicates that MDSC can be a therapeutic target to alleviate their pro-tumourigenic functions and immunosuppressive activities to bolster the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors. In this review, we provide an overview of the general immunotherapeutic approaches and discuss the characterisation, expansion, and activities of MDSCs with the current treatments used to target them either as a single therapeutic target or synergistically in combination with immunotherapy.
Keywords: Myeloid derived suppressor cells; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune system; immunotherapy; tumour microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

